 源码剖析-依赖管理
源码剖析-依赖管理
问题:(1)为什么导入dependency时不需要指定版本?
在Spring Boot入门程序中,项目pom.xml文件有两个核心依赖,分别是spring-boot-starter-parent和spring-boot-starter-web,关于这两个依赖的相关介绍具体如下
# spring-boot-starter-parent
在chapter01项目中的pom.xml文件中找到spring-boot-starter-parent依赖,示例代码如下:
<!-- Spring Boot父项目依赖管理 -->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.9.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
2
3
4
5
6
7
上述代码中,将spring-boot-starter-parent依赖作为Spring Boot项目的统一父项目依赖管理,并将项目版本号统一为2.2.9.RELEASE,该版本号根据实际开发需求是可以修改的
使用“Ctrl+鼠标左键”进入并查看spring-boot-starter-parent底层源文件,先看spring-boot-starter-parent做了哪些事
首先看spring-boot-starter-parent的properties节点
<properties>
<main.basedir>${basedir}/../../..</main.basedir>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<resource.delimiter>@</resource.delimiter> <!-- delimiter that doesn't clash with Spring ${} placeholders -->
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>${java.version}</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>${java.version}</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
在这里spring-boot-starter-parent定义了:
- 工程的Java版本为
1.8。 - 工程代码的编译源文件编码格式为
UTF-8 - 工程编译后的文件编码格式为
UTF-8 - Maven打包编译的版本
再来看spring-boot-starter-parent的「build」节点
接下来看POM的build节点,分别定义了resources资源和pluginManagement
<resources>
<resource>
<filtering>true</filtering>
<directory>${basedir}/src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/application*.yml</include>
<include>**/application*.yaml</include>
<include>**/application*.properties</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>${basedir}/src/main/resources</directory>
<excludes>
<exclude>**/application*.yml</exclude>
<exclude>**/application*.yaml</exclude>
<exclude>**/application*.properties</exclude>
</excludes>
</resource>
</resources>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
我们详细看一下resources节点,里面定义了资源过滤,针对application的yml、properties格式进行了过滤,可以支持支持不同环境的配置,比如application-dev.yml、application-test.yml、application-dev.properties、application-dev.properties等等。
pluginManagement则是引入了相应的插件和对应的版本依赖
最后来看spring-boot-starter-parent的父依赖spring-boot-dependencies
spring-boot-dependencies的properties节点
我们看定义POM,这个才是SpringBoot项目的真正管理依赖的项目,里面定义了SpringBoot相关的版本
<properties>
<main.basedir>${basedir}/../..</main.basedir>
<!-- Dependency versions -->
<activemq.version>5.15.13</activemq.version>
<antlr2.version>2.7.7</antlr2.version>
<appengine-sdk.version>1.9.81</appengine-sdk.version>
<artemis.version>2.10.1</artemis.version>
<aspectj.version>1.9.6</aspectj.version>
<assertj.version>3.13.2</assertj.version>
<atomikos.version>4.0.6</atomikos.version>
<awaitility.version>4.0.3</awaitility.version>
<bitronix.version>2.1.4</bitronix.version>
<byte-buddy.version>1.10.13</byte-buddy.version>
<caffeine.version>2.8.5</caffeine.version>
<cassandra-driver.version>3.7.2</cassandra-driver.version>
<classmate.version>1.5.1</classmate.version>
.......
</properties>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
spring-boot-dependencies的dependencyManagement节点
在这里,dependencies定义了SpringBoot版本的依赖的组件以及相应版本。
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot</artifactId>
<version>${revision}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-test</artifactId>
<version>${revision}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-test-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>${revision}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-actuator</artifactId>
<version>${revision}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-actuator-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>${revision}</version>
</dependency>
....
</dependencyManagement>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
spring-boot-starter-parent通过继承spring-boot-dependencies从而实现了SpringBoot的版本依赖管理,所以我们的SpringBoot工程继承spring-boot-starter-parent后已经具备版本锁定等配置了,这也就是在 Spring Boot 项目中部分依赖不需要写版本号的原因
(2)问题2: spring-boot-starter-parent父依赖启动器的主要作用是进行版本统一管理,那么项目运行依赖的JAR包是从何而来的?
# spring-boot-starter-web
查看spring-boot-starter-web依赖文件源码,核心代码具体如下
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-el</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
从上述代码可以发现,spring-boot-starter-web依赖启动器的主要作用是打包了Web开发场景所需的底层所有依赖(基于依赖传递,当前项目也存在对应的依赖jar包)
正是如此,在pom.xml中引入spring-boot-starter-web依赖启动器时,就可以实现Web场景开发,而不需要额外导入Tomcat服务器以及其他Web依赖文件等。
当然,这些引入的依赖文件的版本号还是由spring-boot-starter-parent父依赖进行的统一管理。
Spring Boot除了提供有上述介绍的Web依赖启动器外,还提供了其他许多开发场景的相关依赖,我们可以打开Spring Boot官方文档,搜索“Starters”关键字查询场景依赖启动器
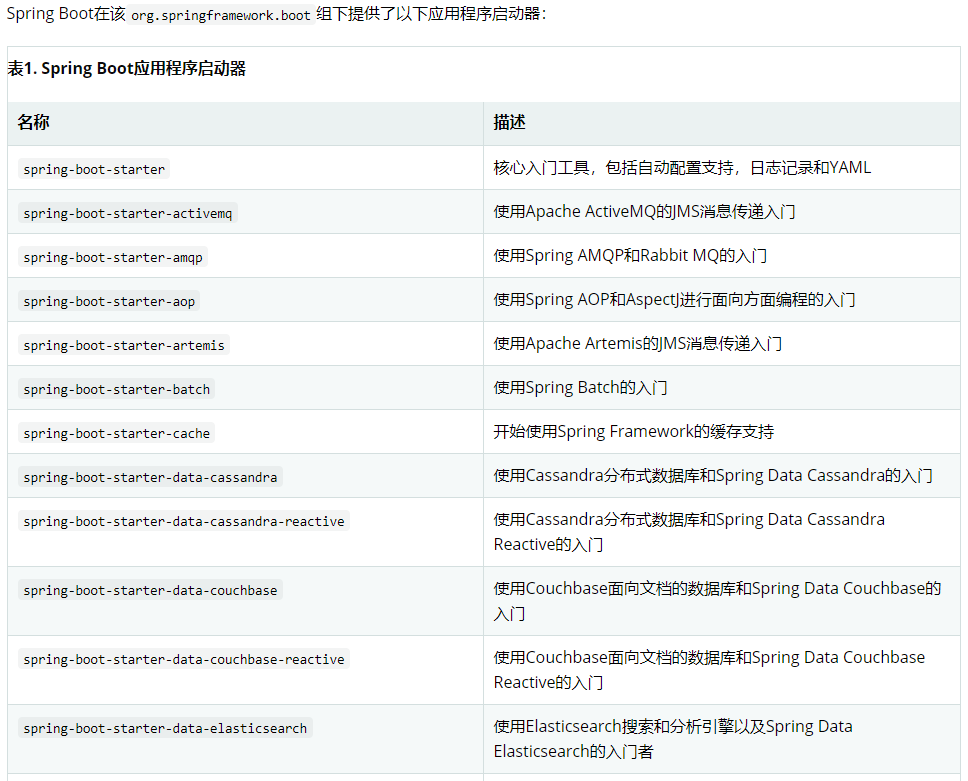
列出了Spring Boot官方提供的部分场景依赖启动器,这些依赖启动器适用于不同的场景开发,使用时只需要在pom.xml文件中导入对应的依赖启动器即可。
需要说明的是,Spring Boot官方并不是针对所有场景开发的技术框架都提供了场景启动器,例如阿里巴巴的Druid数据源等,Spring Boot官方就没有提供对应的依赖启动器。为了充分利用Spring Boot框架的优势,在Spring Boot官方没有整合这些技术框架的情况下,Druid等技术框架所在的开发团队主动与Spring Boot框架进行了整合,实现了各自的依赖启动器,例如druid-spring-boot-starter等。我们在pom.xml文件中引入这些第三方的依赖启动器时,切记要配置对应的版本号

