 TCP粘包拆包的问题及解决
TCP粘包拆包的问题及解决
# 2.1、ReplayingDecoder
在前⾯案例中,当需要获取int数据时,需要进⾏判断是否够4个字节,如果解码业务过于复杂的话,这 样的判断会显得⾮常的繁琐,在Netty中提供了ReplayingDecoder就可以解决这样的问题。 ReplayingDecoder也是继承了ByteToMessageDecoder进⾏的扩展。
javadoc⽂档中的⼀个示例:
public class IntegerHeaderFrameDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf buf, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
if (buf.readableBytes() < 4) {
return;
}
buf.markReaderIndex(); int length = buf.readInt();
if (buf.readableBytes() < length) {
buf.resetReaderIndex(); return;
}
out.add(buf.readBytes(length));
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
使⽤ReplayingDecoder后:
public class IntegerHeaderFrameDecoder extends ReplayingDecoder<Void> {
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf buf, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
out.add(buf.readBytes(buf.readInt()));
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
基本原理:
- 使⽤了特殊的ByteBuf,叫做ReplayingDecoderByteBuf,扩展了ByteBuf
- 重写了ByteBuf的readXxx()等⽅法,会先检查可读字节⻓度,⼀旦检测到不满⾜要求就直接抛出 REPLAY(REPLAY继承ERROR)
- ReplayingDecoder重写了ByteToMessageDecoder的callDecode()⽅法,捕获Signal并在catch块 中重置ByteBuf的readerIndex。 继续等待数据,直到有了数据后继续读取,这样就可以保证读取到需要读取的数据。
- 类定义中的泛型 S 是⼀个⽤于记录解码状态的状态机枚举类,在state(S s)、checkpoint(S s)等⽅ 法中会⽤到。在简单解码时也可以⽤java.lang.Void来占位。
需要注意:
- buffer的部分操作(readBytes(ByteBuffer dst)、retain()、release()等⽅法会直接抛出异常)
- 在某些情况下会影响性能(如多次对同⼀段消息解码)
TCP是基于流的,只保证接收到数据包分⽚顺序,⽽不保证接收到的数据包每个分⽚⼤⼩。因此在使⽤ ReplayingDecoder时,即使不存在多线程,同⼀个线程也可能多次调⽤decode()⽅法。在decode中修 改ReplayingDecoder的类变量时必须⼩⼼谨慎。
//这是⼀个错误的例⼦:
//消息中包含了2个integer,代码中decode⽅法会被调⽤两次,此时队列size不等于2,这段代码达不 到期望结果。
public class MyDecoder extends ReplayingDecoder<Void> {
private final Queue<Integer> values = new LinkedList<Integer>();
@Override public void decode(ByteBuf buf, List<Object> out) throws Exception { // A message contains 2 integers.
values.offer(buf.readInt());
values.offer(buf.readInt());
assert values.size() == 2;
out.add(values.poll() + values.poll());
}
}
//正确的做法:
public class MyDecoder extends ReplayingDecoder<Void> {
private final Queue<Integer> values = new LinkedList<Integer>();
@Override
public void decode(ByteBuf buf, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
// Revert the state of the variable that might have been changed
// since the last partial decode.
values.clear();
// A message contains 2 integers.
values.offer(buf.readInt());
values.offer(buf.readInt()); // Now we know this assertion will never fail.
assert values.size() == 2;
out.add(values.poll() + values.poll());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
ByteToIntegerDecoder2的实现:
package cn.itcast.netty.coder;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.ByteToMessageDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.ReplayingDecoder;
import java.util.List;
public class ByteToIntegerDecoder2 extends ReplayingDecoder < Void > {
/**
* @param ctx 上下⽂
* @param in 输⼊的ByteBuf消息数据
* @param out 转化后输出的容器
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in , List < Object > out) throws Exception {
out.add(in.readInt()); //读取到int类型数据,放⼊到输出,完成数据类型的转化
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
ServerHandler:
package cn.itcast.netty.codec.obj;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
public class ServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler < User > {
@Override
public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, User user) throws
Exception {
//获取到user对象 System.out.println(user);
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("ok", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 2.2、什么是TCP粘包/拆包问题?
TCP是流传递的,所谓流,就是⼀串没有界限的数据,服务端接收到客户端发来的数据,并不确定这是 ⼀条数据,还是多条数据,应该如何拆包,服务端是不知道的。
所以,客户端与服务端就需要约定好拆包的规则,客户端按照此规则进⾏粘包,⽽服务端按照此规则进 ⾏拆包,这就是TCP的粘包与拆包,如果不约定好,就会出现服务端不能按照期望拿到数据。
实际上,彼此约定的规则就是协议,⾃定义协议就是⾃定义规则。
# 2.2.1、案例:演示TCP粘包/拆包问题
客户端:向服务端发送10条消息,并且记录服务端返回的消息的数量。
package cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage.client;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
public class NettyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 服务器启动类
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(worker);
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 5566).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
package cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage.client;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
public class ClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler < ByteBuf > {
private int count;
@Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("接收到服务端的消息:" + msg.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("接收到服务端的消息数量:" + (++count));
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("from client a message!", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
服务端:接收消息并且记录消息的数量,向客户端发送响应。
package cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage.server;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
public class NettyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 主线程,不处理任何业务逻辑,只是接收客户的连接请求
EventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
// ⼯作线程,线程数默认是:cpu*2
EventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 服务器启动类
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker); //配置server通道
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>
() {
@Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
}); //worker线程的处理器
ChannelFuture future = serverBootstrap.bind(5566).sync();
System.out.println("服务器启动完成。。。。。");
//等待服务端监听端⼝关闭
future.channel().closeFuture().sync(); }
finally {
//优雅关闭
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
package cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage.server;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
public class ServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler < ByteBuf > {
private int count;
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("服务端接收到消息:" + msg.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("服务端接收到消息数量:" + (++count));
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("ok", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
测试结果:
#服务端
服务器启动完成。。。。。
服务端接收到消息:from client a message!from client a message!from client a message!from client a message!from client a message!from client a message!from client a message!from client a message!from client a message!from client a message!
服务端接收到消息数量:1
#客户端
接收到服务端的消息:ok 接收到服务端的消息数量:1
#测试结果与期望不符
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 2.3、解决⽅法
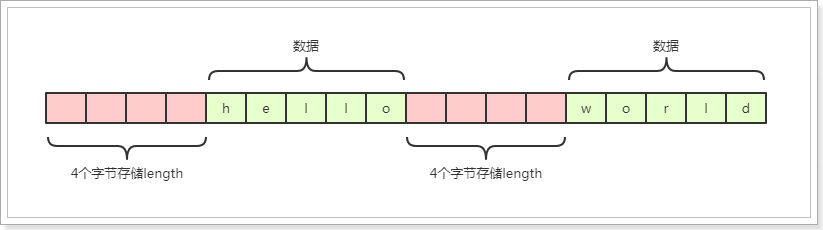
⼀般来讲有3中⽅法解决TCP的粘包与拆包问题:
在发送的数据包中添加头,在头⾥存储数据的⼤⼩,服务端就可以按照此⼤⼩来读取数据,这样就 知道界限在哪⾥了。 以固定的⻓度发送数据,超出的分多次发送,不⾜的以0填充,接收端就以固定⻓度接收即可。 在数据包之间设置边界,如添加特殊符号,这样,接收端通过这个边界就可以将不同的数据包拆分 开。
# 2.4、实战:解决TCP的粘包/拆包问题
# 2.4.1、⾃定义协议
package cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage2;
public class MyProtocol {
private Integer length; //数据头:⻓度
private byte[] body; //数据体
public Integer getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(Integer length) {
this.length = length;
}
public byte[] getBody() {
return body;
}
public void setBody(byte[] body) {
this.body = body;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 2.4.2、编解码器
编码器:
package cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage2;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToByteEncoder;
public class MyEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder < MyProtocol > {
@Override protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MyProtocol msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
out.writeInt(msg.getLength());
out.writeBytes(msg.getBody());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
解码器:
package cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage2;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.ReplayingDecoder;
import java.util.List;
public class MyDecoder extends ReplayingDecoder < Void > {
@Override protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in , List < Object > out) throws Exception {
int length = in.readInt(); //获取⻓度 byte[] data = new byte[length]; //根据⻓度定义byte数组 in.readBytes(data); //读取数据
MyProtocol myProtocol = new MyProtocol();
myProtocol.setLength(length);
myProtocol.setBody(data);
out.add(myProtocol);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 2.4.3、客户端
package cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage2.client;
import cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage2.MyProtocol;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
public class ClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler < MyProtocol > {
private int count;
@Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MyProtocol msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("接收到服务端的消息:" + new String(msg.getBody(), CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("接收到服务端的消息数量:" + (++count));
}
@Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
byte[] data = "from client a message!".getBytes(CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
MyProtocol myProtocol = new MyProtocol();
myProtocol.setLength(data.length);
myProtocol.setBody(data);
ctx.writeAndFlush(myProtocol);
}
}
@Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
package cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage2.client;
import cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage2.MyDecoder;
import cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage2.MyEncoder;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
public class NettyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 服务器启动类
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(worker);
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer < SocketChannel > () {
@Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new MyEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new MyDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 5566).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# 1.5.2**、客户端**
NettyObjectClient:
package cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage2.client;
import cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage2.MyDecoder;
import cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage2.MyEncoder;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
public class NettyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 服务器启动类
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(worker);
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer < SocketChannel > () {
@Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new MyEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new MyDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 5566).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# 2.4.4、服务端
package cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage2.server;
import cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage2.MyProtocol;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
public class ServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler < MyProtocol > {
private int count;
@Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MyProtocol msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("服务端接收到消息:" + new String(msg.getBody(), CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("服务端接收到消息数量:" + (++count));
byte[] data = "ok".getBytes(CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
MyProtocol myProtocol = new MyProtocol();
myProtocol.setLength(data.length);
myProtocol.setBody(data);
ctx.writeAndFlush(myProtocol);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
package cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage2.server;
import cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage2.MyDecoder;
import cn.itcast.netty.tcppackage2.MyEncoder;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
public class NettyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 主线程,不处理任何业务逻辑,只是接收客户的连接请求
EventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); // ⼯作线程,线程数默认是:cpu*2
EventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 服务器启动类
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker); //配置server通道
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer < SocketChannel > () {
@Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new MyDecoder()).addLast(new MyEncoder()).addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
}); //worker线程的处理器
ChannelFuture future = serverBootstrap.bind(5566).sync();
System.out.println("服务器启动完成。。。。。");
//等待服务端监听端⼝关闭
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally { //优雅关闭
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
# 2.4.5、测试
#客户端
接收到服务端的消息:ok
接收到服务端的消息数量:1
接收到服务端的消息:ok
接收到服务端的消息数量:2
接收到服务端的消息:ok
接收到服务端的消息数量:3
接收到服务端的消息:ok
接收到服务端的消息数量:4
接收到服务端的消息:ok
接收到服务端的消息数量:5
接收到服务端的消息:ok
接收到服务端的消息数量:6
接收到服务端的消息:ok
接收到服务端的消息数量:7
接收到服务端的消息:ok
接收到服务端的消息数量:8
接收到服务端的消息:ok
接收到服务端的消息数量:9
接收到服务端的消息:ok
接收到服务端的消息数量:10
#服务端
服务器启动完成。。。。。
服务端接收到消息:from client a message!
服务端接收到消息数量:1
服务端接收到消息:from client a message!
服务端接收到消息数量:2
服务端接收到消息:from client a message!
服务端接收到消息数量:3
服务端接收到消息:from client a message!
服务端接收到消息数量:4
服务端接收到消息:from client a message!
服务端接收到消息数量:5
服务端接收到消息:from client a message!
服务端接收到消息数量:6
服务端接收到消息:from client a message!
服务端接收到消息数量:7
服务端接收到消息:from client a message!
服务端接收到消息数量:8
服务端接收到消息:from client a message!
服务端接收到消息数量:9
服务端接收到消息:from client a message!
服务端接收到消息数量:10
#测试结果符合预期
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46

