 源码剖析-揭秘SqlSession执行主流程
源码剖析-揭秘SqlSession执行主流程
# 7.1 相关类与接口
- DefaultSqlSession:SqlSession接口的默认实现类
- Executor接口
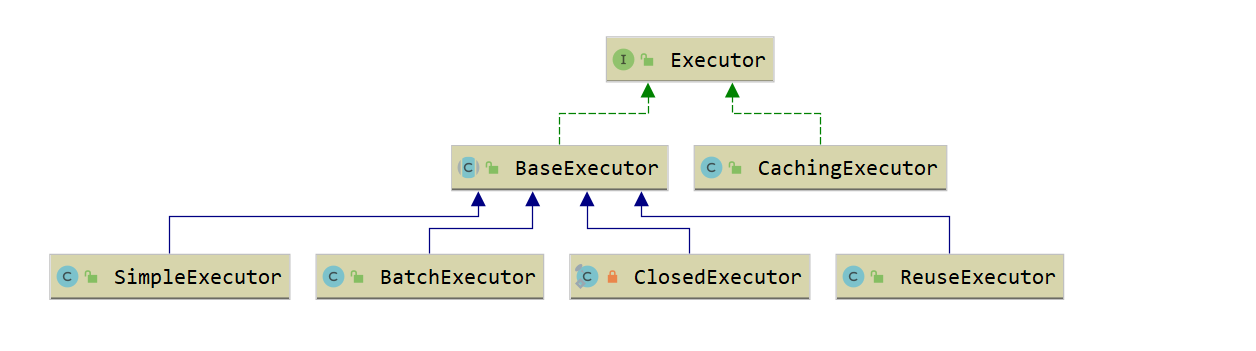
BaseExecutor:基础执行器,封装了子类的公共方法,包括一级缓存、延迟加载、回滚、关闭等功能;
SimpleExecutor:简单执行器,每执行一条 sql,都会打开一个 Statement,执行完成后关闭;
ReuseExecutor:重用执行器,相较于 SimpleExecutor 多了 Statement 的缓存功能,其内部维护一个
Map<String, Statement>,每次编译完成的 Statement 都会进行缓存,不会关闭;BatchExecutor:批量执行器,基于 JDBC 的
addBatch、executeBatch功能,并且在当前 sql 和上一条 sql 完全一样的时候,重用 Statement,在调用doFlushStatements的时候,将数据刷新到数据库;CachingExecutor:缓存执行器,装饰器模式,在开启缓存的时候。会在上面三种执行器的外面包上 CachingExecutor;
StatementHandler接口:
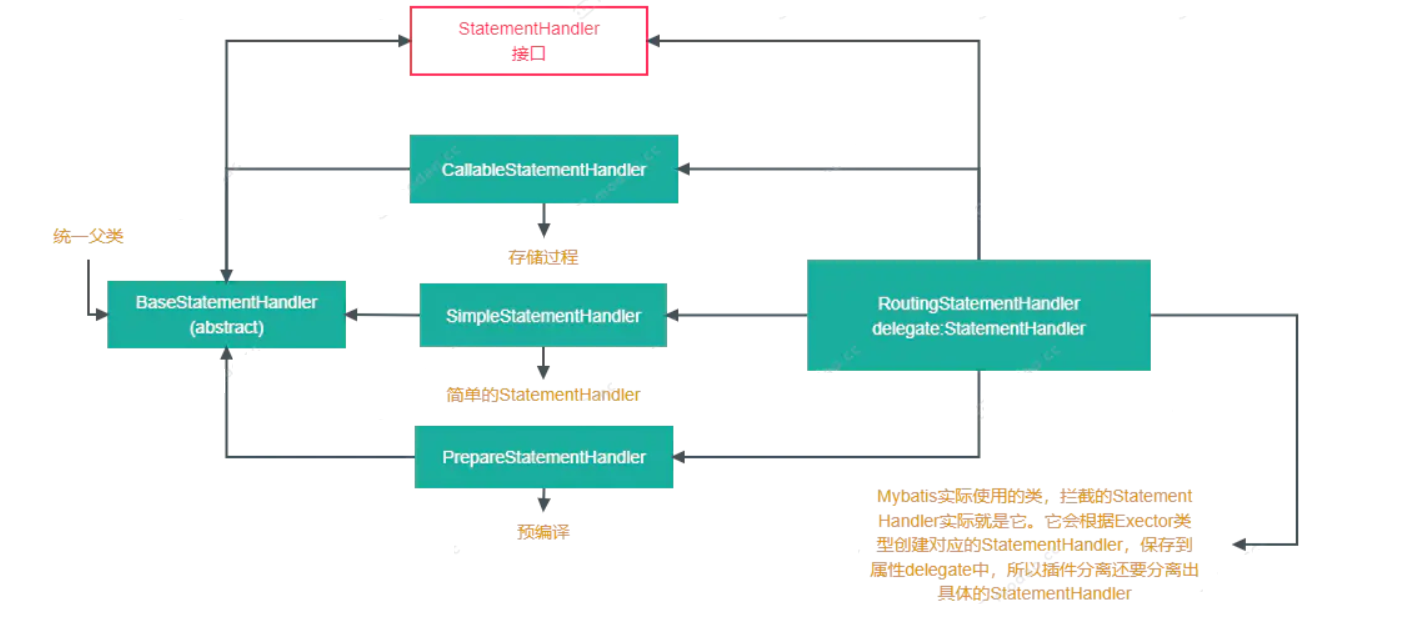
- RoutingStatementHandler:路由。Mybatis实际使用的类,拦截的StatementHandler实际就是它。它会根据Exector类型创建对应的StatementHandler,保存到属性delegate中
- PreparedStatementHandler:预编译Statement
- ResultSetHandler接口:处理Statement执行后产生的结果集,生成结果列表;处理存储过程执行后的输出参数
- DefaultResultSetHandler:ResultSetHandler的 默认实现类
# 7.2 流程分析
# 入口:DefaultSqlSession#selectList
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
// 根据传入的statementId,获取MappedStatement对象
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 调用执行器的查询方法
// RowBounds是用来逻辑分页(按照条件将数据从数据库查询到内存中,在内存中进行分页)
// wrapCollection(parameter)是用来装饰集合或者数组参数
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 1. CachingExecutor#query
Configuration中cacheEnabled属性值默认为true
//第一步
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 获取绑定的SQL语句,比如“SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = ? ”
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 生成缓存Key
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
//第二步
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
// 获取二级缓存
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
// 当为select语句时,flushCache默认为false,表示任何时候语句被调用,都不会去清空本地缓存和二级缓存
// 当为insert、update、delete语句时,useCache默认为true,表示会将本条语句的结果进行二级缓存
// 刷新二级缓存 (存在缓存且flushCache为true时)
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
// 从二级缓存中查询数据
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
// 如果二级缓存中没有查询到数据,则查询数据库
if (list == null) {
// 委托给BaseExecutor执行
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
// 委托给BaseExecutor执行
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
# 2. BaseExecutor#query
二级缓存设置开启且缓存中没有或者未开启二级缓存,则从一级缓存中查找结果集
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
// 从一级缓存中获取数据
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
// 如果一级缓存没有数据,则从数据库查询数据
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
# 3. BaseExecutor#queryFromDatabase
如果一级缓存没有数据,则从数据库查询数据
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
// 执行查询
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
//移除一级缓存中原有值
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
//往一级缓存中存值
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 4. SimpleExecutor#doQuery

- BaseStatementHandler:基础语句处理器(抽象类),它基本把语句处理器接口的核心部分都实现了,包括配置绑定、执行器绑定、映射器绑定、参数处理器构建、结果集处理器构建、语句超时设置、语句关闭等,并另外定义了新的方法 instantiateStatement 供不同子类实现以便获取不同类型的语句连接,子类可以普通执行 SQL 语句,也可以做预编译执行,还可以执行存储过程等。
- SimpleStatementHandler:普通语句处理器,继承 BaseStatementHandler 抽象类,对应 java.sql.Statement 对象的处理,处理普通的不带动态参数运行的 SQL,即执行简单拼接的字符串语句,同时由于 Statement 的特性,SimpleStatementHandler 每次执行都需要编译 SQL (注意:我们知道 SQL 的执行是需要编译和解析的)。
- PreparedStatementHandler:预编译语句处理器,继承 BaseStatementHandler 抽象类,对应 java.sql.PrepareStatement 对象的处理,相比上面的普通语句处理器,它支持可变参数 SQL 执行,由于 PrepareStatement 的特性,它会进行预编译,在缓存中一旦发现有预编译的命令,会直接解析执行,所以减少了再次编译环节,能够有效提高系统性能,并预防 SQL 注入攻击(所以是系统默认也是我们推荐的语句处理器)。
- CallableStatementHandler:存储过程处理器,继承 BaseStatementHandler 抽象类,对应 java.sql.CallableStatement 对象的处理,很明了,它是用来调用存储过程的,增加了存储过程的函数调用以及输出/输入参数的处理支持。
- RoutingStatementHandler:路由语句处理器,直接实现了 StatementHandler 接口,作用如其名称,确确实实只是起到了路由功能,并把上面介绍到的三个语句处理器实例作为自身的委托对象而已,所以执行器在构建语句处理器时,都是直接 new 了 RoutingStatementHandler 实例。
执行查询
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler,
BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// 获取Configuration对象
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 创建RoutingStatementHandler,用来处理Statement
// RoutingStatementHandler类中初始化delegate类(SimpleStatementHandler、PreparedStatementHandler)
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds,
resultHandler, boundSql);
// 子流程1:设置参数
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 子流程2:执行SQL语句(已经设置过参数),并且映射结果集
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# 4.1 Configuration#newStatementHandler
创建StatementHandler,用来执行MappedStatement对象
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement,
Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
// 创建路由功能的StatementHandler,根据MappedStatement中的StatementType
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject,
rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 4.1.1 RoutingStatementHandler#构造函数
创建路由功能的StatementHandler,根据MappedStatement中的StatementType
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
switch (ms.getStatementType()) {
case STATEMENT:
delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case PREPARED:
delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case CALLABLE:
delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
default:
throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 4.2 SimpleExecutor#prepareStatement
设置参数
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
// 获取连接
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 创建Statement(PreparedStatement、Statement、CallableStatement)
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// SQL参数设置
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 4.2.1 BaseExecutor#getConnection
获取数据库连接
protected Connection getConnection(Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = transaction.getConnection();
if (statementLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
return ConnectionLogger.newInstance(connection, statementLog, queryStack);
} else {
return connection;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 4.2.2 BaseStatementHandler#prepare
创建Statement(PreparedStatement、Statement、CallableStatement)
@Override
public Statement prepare(Connection connection, Integer transactionTimeout) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().sql(boundSql.getSql());
Statement statement = null;
try {
// 实例化Statement,比如PreparedStatement
statement = instantiateStatement(connection);
// 设置查询超时时间
setStatementTimeout(statement, transactionTimeout);
setFetchSize(statement);
return statement;
} catch (SQLException e) {
closeStatement(statement);
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
closeStatement(statement);
throw new ExecutorException("Error preparing statement. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# 4.2.2.1 PreparedStatementHandler#instantiateStatement
实例化PreparedStatement
@Override
protected Statement instantiateStatement(Connection connection) throws SQLException {
// 获取带有占位符的SQL语句
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
// 处理带有主键返回的SQL
if (mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator() instanceof Jdbc3KeyGenerator) {
String[] keyColumnNames = mappedStatement.getKeyColumns();
if (keyColumnNames == null) {
return connection.prepareStatement(sql, PreparedStatement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
} else {
return connection.prepareStatement(sql, keyColumnNames);
}
} else if (mappedStatement.getResultSetType() == ResultSetType.DEFAULT) {
return connection.prepareStatement(sql);
} else {
return connection.prepareStatement(sql, mappedStatement.getResultSetType().getValue(), ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 4.2.3 PreparedStatementHandler#parameterize
SQL参数设置,参数映射流程会详细分解
@Override
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
// 通过ParameterHandler处理参数
parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);
}
2
3
4
5
# 4.3 PreparedStatementHandler#query
执行SQL语句(已经设置过参数),并且映射结果集
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
// 执行PreparedStatement,也就是执行SQL语句
ps.execute();
// 处理结果集
return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 4.3.1 PreparedStatement#execute
调用JDBC的api执行Statement
# 4.3.2 DefaultResultSetHandler#handleResultSets
处理结果集 ,结果映射流程会详细分解
@Override
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId());
// <select>标签的resultMap属性,可以指定多个值,多个值之间用逗号(,)分割
final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<>();
int resultSetCount = 0;
// 这里是获取第一个结果集,将传统JDBC的ResultSet包装成一个包含结果列元信息的ResultSetWrapper对象
ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt);
// 这里是获取所有要映射的ResultMap(按照逗号分割出来的)
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
// 要映射的ResultMap的数量
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
// 循环处理每个ResultMap,从第一个开始处理
while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
// 得到结果映射信息
ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
// 处理结果集
// 从rsw结果集参数中获取查询结果,再根据resultMap映射信息,将查询结果映射到multipleResults中
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null);
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
// 对应<select>标签的resultSets属性,一般不使用该属性
String[] resultSets = mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while (rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
}
// 如果只有一个结果集合,则直接从多结果集中取出第一个
return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
四、总结
# 执行sqlsession:参数有两个(statementId和参数对象)
- 根据statementId,去Configuration中的MappedStatement集合中查找 对应的MappedStatement对象;
- 取出MappedStatement中的SQL信息;
- 取出MappedStatement中的statementType,用来创建Statement对象;
- 取出MappedStatement中的Configuration对象,通过Configuration对象,获取DataSource对象,通过DataSource对象,创建Connection,通过Connection创建Statement对象。
- 设置参数
- 执行Statement
- 处理结果集

