 3 Elasticsearch高级应用
3 Elasticsearch高级应用
# 1 映射高级
# 1.1 地理坐标点数据类型
# 1.1.1 地理坐标点
地理坐标点是指地球表面可以用经纬度描述的一个点。 地理坐标点可以用来计算两个坐标间的距离,还可以判断一个坐标是否在一个区域中。地理坐标点需要显式声明对应字段类型为 geo_point :
示例
PUT /company-locations
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"location": {
"type": "geo_point"
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 1.1.2 经纬度坐标格式
如上例, location 字段被声明为 geo_point 后,我们就可以索引包含了经纬度信息的文档了。 经纬度信息的形式可以是字符串、数组或者对象
# 字符串形式
PUT /company-locations/_doc/1
{
"name":"NetEase",
"location":"40.715,74.011"
}
# 对象形式
PUT /company-locations/_doc/2
{
"name":"Sina",
"location":{
"lat":40.722,
"lon":73.989
}
}
# 数组形式
PUT /company-locations/_doc/3
{
"name":"Baidu",
"location":[73.983,40.719]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
注意
字符串形式以半角逗号分割,如 "lat,lon"
对象形式显式命名为 lat 和 lon
数组形式表示为 [lon,lat]
# 1.1.3 通过地理坐标点过滤
有四种地理坐标点相关的过滤器 可以用来选中或者排除文档
| 过滤器 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| geo_bounding_box | 找出落在指定矩形框中的点 |
| geo_distance | 找出与指定位置在给定距离内的点 |
| geo_distance_range | 找出与指定点距离在给定最小距离和最大距离之间的点 |
| geo_polygon | 找出落在多边形中的点。 这个过滤器使用代价很大 。当你觉得自己需要使用它,最好先看看 geo-shapes 。 |
# 1.1.4 geo_bounding_box查询
这是目前为止最有效的地理坐标过滤器了,因为它计算起来非常简单。 你指定一个矩形的顶部 ,
底部 , 左边界和右边界,然后过滤器只需判断坐标的经度是否在左右边界之间,纬度是否在上下边
界之间
然后可以使用 geo_bounding_box 过滤器执行以下查询
GET /company-locations/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"match_all": {}
},
"filter": {
"geo_bounding_box": {
"location": {
"top_left": {
"lat": 40.73,
"lon": 71.12
},
"bottom_right": {
"lat": 40.01,
"lon": 74.1
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
location这些坐标也可以用 bottom_left 和 top_right 来表示
# 1.1.5 geo_distance
过滤仅包含与地理位置相距特定距离内的匹配的文档。假设以下映射和索引文档
然后可以使用 geo_distance 过滤器执行以下查询
GET /company-locations/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"match_all": {}
},
"filter": {
"geo_distance": {
"distance": "200km",
"location": {
"lat": 40,
"lon": 70
}
}
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# 1.2.动态映射
Elasticsearch在遇到文档中以前未遇到的字段,可以使用dynamic mapping(动态映射机制) 来确定字段的数据类型并自动把新的字段添加到类型映射。
Elastic的动态映射机制可以进行开关控制,通过设置mappings的dynamic属性,dynamic有如下设置项
- true:遇到陌生字段就执行dynamic mapping处理机制
- false:遇到陌生字段就忽略
- strict:遇到陌生字段就报错
# 设置为报错
PUT /user
{
"settings":{
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 0
},
"mappings":{
"dynamic": "strict",
"properties": {
"name": {"type": "text"},
"address": {"type": "object", "dynamic": true}
}
}
}
# 插入以下文档,将会报错
# user索引层设置dynamic是strict,在user层内设置age将报错
# 在address层设置dynamic是ture,将动态映射生成字段
PUT /user/_doc/1
{
"name": "lisi",
"age": "20",
"address": {
"province": "beijing",
"city": "beijing"
}
}
PUT /user
{
"settings":{
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 0
},
"mappings":{
"dynamic": true,
"properties": {
"name": {"type": "text"},
"address": {"type": "object", "dynamic": true}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
# 1.3 自定义动态映射
如果你想在运行时增加新的字段,你可能会启用动态映射。 然而,有时候,动态映射 规则 可能不太智能。幸运的是,我们可以通过设置去自定义这些规则,以便更好的适用于你的数据。
# 1.3.1 日期检测
当 Elasticsearch 遇到一个新的字符串字段时,它会检测这个字段是否包含一个可识别的日期,比如2014-01-01 如果它像日期,这个字段就会被作为 date 类型添加。否则,它会被作为 string 类型添加。
有些时候这个行为可能导致一些问题。想象下,你有如下这样的一个文档:
{ "note": "2014-01-01" }
假设这是第一次识别 note 字段,它会被添加为 date 字段。但是如果下一个文档像这样:
{ "note": "Logged out" }
这显然不是一个日期,但为时已晚。这个字段已经是一个日期类型,这个 不合法的日期 将会造成一个异常。
日期检测可以通过在根对象上设置 date_detection 为 false 来关闭
PUT /my_index/_doc/1
{ "note": "2014-01-01" }
PUT /my_index/_doc/1
{ "note": "Logged out" }
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"date_detection": false
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
使用这个映射,字符串将始终作为 string 类型。如果需要一个 date 字段,必须手动添加。
Elasticsearch 判断字符串为日期的规则可以通过 dynamic_date_formats setting 来设置。
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic_date_formats": "MM/dd/yyyy"
}
}
PUT /my_index/_doc/1
{ "note": "2014-01-01" }
PUT /my_index/_doc/1
{ "note": "01/01/2014" }
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 1.3.2 dynamic_templates
使用 dynamic_templates 可以完全控制新生成字段的映射,甚至可以通过字段名称或数据类型来应用不同的映射。每个模板都有一个名称,你可以用来描述这个模板的用途,一个 mapping 来指定映射应该怎样使用,以及至少一个参数 (如 match) 来定义这个模板适用于哪个字段。
模板按照顺序来检测;第一个匹配的模板会被启用。例如,我们给 string 类型字段定义两个模板:
es :以 _es 结尾的字段名需要使用 spanish 分词器。
en :所有其他字段使用 english 分词器。
我们将 es 模板放在第一位,因为它比匹配所有字符串字段的 en 模板更特殊:
PUT /my_index2
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"es": {
"match": "*_es",
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"mapping": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "spanish"
}
}
},
{
"en": {
"match": "*",
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"mapping": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "english"
}
}
}
]
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
PUT
/my_index2/_doc/1
{
"name_es":"testes",
"name":"es"
}
2
3
4
5
6
1)匹配字段名以 _es 结尾的字段
2)匹配其他所有字符串类型字段
match_mapping_type 允许你应用模板到特定类型的字段上,就像有标准动态映射规则检测的一样 (例如 string 或 long)
match参数只匹配字段名称,path_match 参数匹配字段在对象上的完整路径,所以 address.*.name将匹配这样的字段
{
"address": {
"city": {
"name": "New York"
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 2 Query DSL
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.3/query-dsl.html
Elasticsearch提供了基于JSON的完整查询DSL(Domain Specific Language 特定域的语言)来定义查询。将查询DSL视为查询的AST(抽象语法树),它由两种子句组成:
- 叶子查询子句
叶子查询子句 在特定域中寻找特定的值,如 match,term或 range查询。
- 复合查询子句
复合查询子句包装其他叶子查询或复合查询,并用于以逻辑方式组合多个查询(例如 bool或
dis_max查询),或更改其行为(例如 constant_score查询)。
我们在使用ElasticSearch的时候,避免不了使用DSL语句去查询,就像使用关系型数据库的时候要学会SQL语法一样。如果我们学习好了DSL语法的使用,那么在日后使用和使用Java Client调用时候也会变得非常简单。
基本语法
POST /索引库名/_search
{
"query": {
"查询类型": {
"查询条件": "查询条件值"
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
这里的query代表一个查询对象,里面可以有不同的查询属性
- 查询类型:
例如: match_all , match , term , range 等等
- 查询条件:查询条件会根据类型的不同,写法也有差异,后面详细讲解
# 2.1 查询所有(match_all query)
示例
POST /lagou-company-index/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
- query :代表查询对象
- match_all :代表查询所有
结果
took:查询花费时间,单位是毫秒
time_out:是否超时
_shards:分片信息
hits:搜索结果总览对象
total:搜索到的总条数
max_score:所有结果中文档得分的最高分
hits:搜索结果的文档对象数组,每个元素是一条搜索到的文档信息
- _index:索引库
- _type:文档类型
- _id:文档id
- _score:文档得分
- _source:文档的源数据
# 2.2 全文搜索(full-text query)
全文搜索能够搜索已分析的文本字段,如电子邮件正文,商品描述等。使用索引期间应用于字段的同一分析器处理查询字符串。全文搜索的分类很多 几个典型的如下:
# 2.2.1 匹配搜索(match query)
全文查询的标准查询,它可以对一个字段进行模糊、短语查询。 match queries 接收
text/numerics/dates, 对它们进行分词分析, 再组织成一个boolean查询。可通过operator 指定bool组合操作(or、and 默认是 or )。
现在,索引库中有2部手机,1台电视;
PUT /lagou-property
{
"settings": {},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"images": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"price": {
"type": "float"
}
}
}
}
POST /lagou-property/_doc/
{
"title": "小米电视4A",
"images": "http://image.lagou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 4288
}
POST /lagou-property/_doc/
{
"title": "小米手机",
"images": "http://image.lagou.com/12479622.jpg",
"price": 2699
}
POST /lagou-property/_doc/
{
"title": "华为手机",
"images": "http://image.lagou.com/12479922.jpg",
"price": 5699
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
# or关系
match 类型查询,会把查询条件进行分词,然后进行查询,多个词条之间是or的关系
POST /lagou-property/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "小米电视4A"
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
结果:
{
"took": 695,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 2,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 2.8330114,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "lagou-property",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "UKcMCnQB7BOR-NcQDHX4",
"_score": 2.8330114,
"_source": {
"title": "小米电视4A",
"images": "http://image.lagou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 4288
}
},
{
"_index": "lagou-property",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "UacMCnQB7BOR-NcQGnUb",
"_score": 0.52354836,
"_source": {
"title": "小米手机",
"images": "http://image.lagou.com/12479622.jpg",
"price": 2699
}
}
]
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
在上面的案例中,不仅会查询到电视,而且与小米相关的都会查询到,多个词之间是 or 的关系。
# and关系
某些情况下,我们需要更精确查找,我们希望这个关系变成 and ,可以这样做:
POST /lagou-property/_search
{"query": {"match": {
"title": {"query": "小米电视4A","operator": "and"}
}}}
2
3
4
结果:
{
"took": 20,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 2.8330114,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "lagou-property",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "UKcMCnQB7BOR-NcQDHX4",
"_score": 2.8330114,
"_source": {
"title": "小米电视4A",
"images": "http://image.lagou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 4288
}
}
]
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# 2.2.2 短语搜索(match phrase query)
match_phrase 查询用来对一个字段进行短语查询,可以指定 analyzer、slop移动因子
GET /lagou-property/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"title": "小米电视"
}
}
}
GET /lagou-property/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"title": "小米 4A"
}
}
}
GET /lagou-property/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"title": {
"query": "小米 4A",
"slop": 2
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# 2.2.3 query_string 查询
Query String Query提供了无需指定某字段而对文档全文进行匹配查询的一个高级查询,同时可以指定在哪些字段上进行匹配。
# 默认 和 指定字段
GET /lagou-property/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string" : {
"query" : "2699"
}
}
}
GET /lagou-property/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string" : {
"query" : "2699",
"default_field" : "title"
}
}
}
# 逻辑查询
GET /lagou-property/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string" : {
"query" : "手机 OR 小米",
"default_field" : "title"
}
}
}
GET /lagou-property/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string" : {
"query" : "手机 AND 小米",
"default_field" : "title"
}
}
}
# 模糊查询
GET /lagou-property/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string" : {
"query" : "大米~1",
"default_field" : "title"
}
}
}
# 多字段支持
GET /lagou-property/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string" : {
"query":"2699",
"fields": [ "title","price"]
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
# 2.2.4 多字段匹配搜索(multi match query)
如果你需要在多个字段上进行文本搜索,可用multi_match 。multi_match在 match的基础上支持对多个字段进行文本查询。
GET /lagou-property/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match" : {
"query":"2699",
"fields": [ "title","price"]
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
还可以使用*匹配多个字段:
GET /lagou-property/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match" : {
"query":"http://image.lagou.com/12479622.jpg",
"fields": [ "title","ima*"]
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 2.3 词条级搜索(term-level queries)
可以使用term-level queries根据结构化数据中的精确值查找文档。结构化数据的值包括日期范围、IP地址、价格或产品ID。
与全文查询不同,term-level queries不分析搜索词。相反,词条与存储在字段级别中的术语完全匹
配。
PUT /book
{
"settings": {},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"description": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"name": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"price": {
"type": "float"
},
"timestamp": {
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss||yyyy-MM-dd||epoch_millis"
}
}
}
}
PUT /book/_doc/1
{
"name": "lucene",
"description": "Lucene Core is a Java library providing powerful indexing and search features, as well as spellchecking, hit highlighting and advanced analysis/tokenization capabilities. The PyLucene sub project provides Python bindings for Lucene Core. ",
"price": 100.45,
"timestamp": "2020-08-21 19:11:35"
}
PUT /book/_doc/2
{
"name": "solr",
"description": "Solr is highly scalable, providing fully fault tolerant distributed indexing, search and analytics. It exposes Lucenes features through easy to use JSON/HTTP interfaces or native clients for Java and other languages.",
"price": 320.45,
"timestamp": "2020-07-21 17:11:35"
}
PUT /book/_doc/3
{
"name": "Hadoop",
"description": "The Apache Hadoop software library is a framework that allows for the distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of computers using simple programming models.",
"price": 620.45,
"timestamp": "2020-08-22 19:18:35"
}
PUT /book/_doc/4
{
"name": "ElasticSearch",
"description": "Elasticsearch是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器。它提供了一个分布式多用户能力的全文搜索引擎,基于RESTful web接口。Elasticsearch是用Java语言开发的,并作为Apache许可条款下的开放源码发布,是一种流行的企业级搜索引擎。Elasticsearch用于云计算中,能够达到实时搜索,稳定,可靠,快速,安装使用方便。官方客户端在Java、.NET(C#)、PHP、Python、Apache Groovy、Ruby和许多其他语言中都是可用的。根据DB-Engines的排名显示,Elasticsearch是最受欢迎的企业搜索引擎,其次是Apache Solr,也是基于Lucene。",
"price": 999.99,
"timestamp": "2020-08-15 10:11:35"
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
# 1) 词条搜索(term query)
term 查询用于查询指定字段包含某个词项的文档
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"term" : { "name" : "solr" }
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
# 2) 词条集合搜索(terms query)
terms 查询用于查询指定字段包含某些词项的文档
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"terms" : { "name" : ["solr", "elasticsearch"]}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
# 3) 范围搜索(range query)
- gte:大于等于
- gt:大于
- lte:小于等于
- lt:小于
- boost:查询权重
GET /book/_search{
"query": {
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 10,
"lte": 200,
"boost": 2
}
}
}
}
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"timestamp": {
"gte": "now-2d/d",
"lt": "now/d"
}
}
}
}
GET book/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"timestamp": {
"gte": "18/08/2020",
"lte": "2021",
"format": "dd/MM/yyyy||yyyy"
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
# 4) 不为空搜索(exists query)
查询指定字段值不为空的文档。相当 SQL 中的 column is not null
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"exists" : { "field" : "price" }
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
# 5) 词项前缀搜索(prefix query)
GET /book/_search
{ "query": {
"prefix" : { "name" : "so" }
}
}
2
3
4
5
# 6) 通配符搜索(wildcard query)
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard" : { "name" : "so*r" }
}
}
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"name": {
"value": "lu*",
"boost": 2
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 7) 正则搜索(regexp query)
regexp允许使用正则表达式进行term查询.注意regexp如果使用不正确,会给服务器带来很严重的性能压力。比如.*开头的查询,将会匹配所有的倒排索引中的关键字,这几乎相当于全表扫描,会很慢。因此如果可以的话,最好在使用正则前,加上匹配的前缀。
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"regexp": {
"name": "s.*"
}
}
}
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"regexp": {
"name": {
"value": "s.*",
"boost": 1.2
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 8) 模糊搜索(fuzzy query)
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"name": "so"
}
}
}
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"name": {
"value": "so",
"boost": 1,
"fuzziness": 2
}
}
}
}
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"name": {
"value": "sorl",
"boost": 1,
"fuzziness": 2
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
# 9) ids搜索(id集合查询)
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"ids": {
"type": "_doc",
"values": [
"1",
"3"
]
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 2.4 复合搜索(compound query)
# 1) constant_score query
用来包装另一个查询,将查询匹配的文档的评分设为一个常值
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"term" : { "description" : "solr"}
}
}
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"term": {
"description": "solr"
}
},
"boost": 1.2
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 2) 布尔搜索(bool query)
bool 查询用bool操作来组合多个查询字句为一个查询。 可用的关键字:
- must:必须满足
- filter:必须满足,但执行的是filter上下文,不参与、不影响评分
- should:或
- must_not:必须不满足,在filter上下文中执行,不参与、不影响评分
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"match": {
"description": "java"
}
},
"filter": {
"term": {
"name": "solr"
}
},
"must_not": {
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 200,
"lte": 300
}
}
},
"minimum_should_match": 1,
"boost": 1
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
minimum_should_match代表了最小匹配精度,如果设置minimum_should_match=1,那么should语句中至少需要有一个条件满足。
# 2.5 排序
# 2.5.1 相关性评分排序
默认情况下,返回的结果是按照 相关性 进行排序的——最相关的文档排在最前。 在本章的后面部
分,我们会解释 相关性 意味着什么以及它是如何计算的, 不过让我们首先看看 sort 参数以及如
何使用它。
为了按照相关性来排序,需要将相关性表示为一个数值。在 Elasticsearch 中, 相关性得分 由一
个浮点数进行表示,并在搜索结果中通过 _score 参数返回, 默认排序是 _score 降序,按照相
关性评分升序排序如下
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {"description":"solr"}
}
}
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {"description":"solr"}
},
"sort": [
{"_score": {"order": "asc"}}
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 2.5.2 字段值排序
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
{"price": {"order": "desc"}}
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 2.5.3 多级排序
假定我们想要结合使用 price和 _score(得分) 进行查询,并且匹配的结果首先按照价格排序,
然后按照相关性得分排序:
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
{
"price": {
"order": "desc"
}
},
{
"timestamp": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 2.6 分页
Elasticsearch中实现分页的语法非常简单:
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"size": 2,
"from": 0
}
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
{
"price": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
],
"size": 2,
"from": 2
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
size:每页显示多少条
from:当前页起始索引, int start = (pageNum - 1) * size
# 2.7 高亮
Elasticsearch中实现高亮的语法比较简单:
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "elasticsearch"
}
},
"highlight": {
"pre_tags": "<font color='pink'>",
"post_tags": "</font>",
"fields": [
{
"name": {}
}
]
}
}
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "elasticsearch"
}
},
"highlight": {
"pre_tags": "<font color='pink'>",
"post_tags": "</font>",
"fields": [
{
"name": {}
},
{
"description": {}
}
]
}
}
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"query": "elasticsearch"
}
},
"highlight": {
"pre_tags": "<font color='pink'>",
"post_tags": "</font>",
"fields": [
{
"name": {}
},
{
"description": {}
}
]
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
在使用match查询的同时,加上一个highlight属性:
pre_tags:前置标签
post_tags:后置标签
fields:需要高亮的字段
- name:这里声明title字段需要高亮,后面可以为这个字段设置特有配置,也可以空
结果:
{
"took": 7,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1.6153753,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 1.6153753,
"_source": {
"name": "ElasticSearch",
"description": "Elasticsearch是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器。它提供了一个分布式多用户能力的全文搜索引擎,基于RESTful web接口。Elasticsearch是用Java语言开发的,并作为Apache许可条款下的开放源码发布,是一种流行的企业级搜索引擎。Elasticsearch用于云计算中,能够达到实时搜索,稳定,可靠,快速,安装使用方便。官方客户端在Java、.NET(C#)、PHP、Python、Apache Groovy、Ruby和许多其他语言中都是可用的。根据DB-Engines的排名显示,Elasticsearch是最受欢迎的企业搜索引擎,其次是Apache Solr,也是基于Lucene。",
"price": 999.99,
"timestamp": "2020-08-15 10:11:35"
},
"highlight": {
"name": [
"<font color='pink'>ElasticSearch</font>"
],
"description": [
"<font color='pink'>Elasticsearch</font>是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器。它提供了一个分布式多用户能力的全文搜索引擎,基于RESTful web接口。",
"<font color='pink'>Elasticsearch</font>是用Java语言开发的,并作为Apache许可条款下的开放源码发布,是一种流行的企业级搜索引擎。",
"<font color='pink'>Elasticsearch</font>用于云计算中,能够达到时搜索,稳定,可靠,快速,安装使用方便。",
"根据DB-Engines的排名显示,<font color='pink'>Elasticsearch</font>是最受欢迎的企业搜索引擎,其次是Apache Solr,也是基于Lucene。"
]
}
}
]
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
# 2.8 文档批量操作(bulk 和 mget)
# 2.8.1 mget 批量查询
单条查询 GET /test_index/_doc/1,如果查询多个id的文档一条一条查询,网络开销太大。
GET /_mget
{
"docs" : [
{
"_index" : "book",
"_id" : 1
},
{
"_index" : "book",
"_id" : 2
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
返回:
{
"docs": [
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 1,
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"name": "lucene",
"description": "Lucene Core is a Java library providing powerful indexing and search features, as well as spellchecking, hit highlighting and advanced analysis/tokenization capabilities. The PyLucene sub project provides Python bindings for Lucene Core. ",
"price": 100.45,
"timestamp": "2020-08-21 19:11:35"
}
},
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "2",
"_version": 1,
"_seq_no": 1,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"name": "solr",
"description": "Solr is highly scalable, providing fully fault tolerant distributed indexing, search and analytics. It exposes Lucenes features through easy to use JSON/HTTP interfaces or native clients for Java and other languages.",
"price": 320.45,
"timestamp": "2020-07-21 17:11:35"
}
}
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
同一索引下批量查询:
GET /book/_mget
{
"docs": [
{
"_id": 2
},
{
"_id": 3
}
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
搜索简化写法
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"ids": {
"values": [
"1",
"4"
]
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 2.8.2 bulk 批量增删改
Bulk 操作解释将文档的增删改查一些列操作,通过一次请求全都做完。减少网络传输次数。
语法:
POST /_bulk
{"action": {"metadata"}}
{"data"}
2
3
如下操作,删除1,新增5,修改2。
POST /_bulk
{ "delete": { "_index": "book", "_id": "1" }}
{ "create": { "_index": "book", "_id": "5" }}
{ "name": "test14","price":100.99 }
{ "update": { "_index": "book", "_id": "2"} }
{ "doc" : {"name" : "test"} }
2
3
4
5
6
功能:
- delete:删除一个文档,只要1个json串就可以了 删除的批量操作不需要请求体
- create:相当于强制创建 PUT /index/type/id/_create
- index:普通的put操作,可以是创建文档,也可以是全量替换文档
- update:执行的是局部更新partial update操作
格式:每个json不能换行。相邻json必须换行。
隔离:每个操作互不影响。操作失败的行会返回其失败信息。
实际用法:bulk请求一次不要太大,否则一下积压到内存中,性能会下降。所以,一次请求几千个操
作、大小在几M正好。
bulk会将要处理的数据载入内存中,所以数据量是有限的,最佳的数据两不是一个确定的数据,它取决于你的硬件,你的文档大小以及复杂性,你的索引以及搜索的负载。
一般建议是1000-5000个文档,大小建议是5-15MB,默认不能超过100M,可以在es的配置文件(ES的config下的elasticsearch.yml)中配置。
http.max_content_length: 10mb
# 3 Filter DSL
Elasticsearch中的所有的查询都会触发相关度得分的计算。对于那些我们不需要相关度得分的场景下,Elasticsearch以过滤器的形式提供了另一种查询功能,过滤器在概念上类似于查询,但是它们有非常快的执行速度,执行速度快主要有以下两个原因:
- 过滤器不会计算相关度的得分,所以它们在计算上更快一些。
- 过滤器可以被缓存到内存中,这使得在重复的搜索查询上,其要比相应的查询快出许多。
为了理解过滤器,可以将一个查询(像是match_all,match,bool等)和一个过滤器结合起来。我们
以范围过滤器为例,它允许我们通过一个区间的值来过滤文档。这通常被用在数字和日期的过滤上。
下面这个例子使用一个被过滤的查询,其返回price值是在200到1000之间(闭区间)的书。
示例
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"filtered": {
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"filter": {
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 200,
"lte": 1000
}
}
}
}
}
}
#5.0 之后的写法
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"match_all": {}
},
"filter": {
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 200,
"lte": 1000
}
}
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
分解上面的例子,被过滤的查询包含一个match_all查询(查询部分)和一个过滤器(filter部分)。我
们可以在查询部分中放入其他查询,在filter部分放入其它过滤器。在上面的应用场景中,由于所有的在这个范围之内的文档都是平等的(或者说相关度都是一样的),没有一个文档比另一个文档更相关,所以这个时候使用范围过滤器就非常合适了。通常情况下,要决定是使用过滤器还是使用查询,你就需要问自己是否需要相关度得分。如果相关度是不重要的,使用过滤器,否则使用查询。查询和过滤器在概念上类似于SELECT WHERE语句。
# 4 定位非法搜索及原因
在开发的时候,我们可能会写到上百行的查询语句,如果出错的话,找起来很麻烦,Elasticsearch提供了帮助开发人员定位不合法的查询的api _validate
示例
GET /book/_search?explain
{
"query": {
"match1": {
"name": "test"
}
}
}
使用 validate
GET /book/_validate/query?explain
{
"query": {
"match1": {
"name": "test"
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
返回结果
{
"valid":false,
"error":"org.elasticsearch.common.ParsingException: no [query] registered for [match1]"
}
2
3
4
在查询时,不小心把 match 写成了 match1 ,通过 validate api 可以清楚的看到错误原因
正确查询返回
{
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"valid": true,
"explanations": [
{
"index": "book",
"valid": true,
"explanation": "name:test"
}
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 5 聚合分析
# 5.1 聚合介绍
聚合分析是数据库中重要的功能特性,完成对一个查询的数据集中数据的聚合计算,如:找出某字段
(或计算表达式的结果)的最大值、最小值,计算和、平均值等。Elasticsearch作为搜索引擎兼数据库,同样提供了强大的聚合分析能力。
对一个数据集求最大、最小、和、平均值等指标的聚合,在ES中称为指标聚合 metric
而关系型数据库中除了有聚合函数外,还可以对查询出的数据进行分组group by,再在组上进行指标聚合。在 ES 中group by 称为分桶,桶聚合 bucketing
Elasticsearch聚合分析语法
在查询请求体中以aggregations节点按如下语法定义聚合分析:
"aggregations" : {
"<aggregation_name>" : { <!--聚合的名字 -->
"<aggregation_type>" : { <!--聚合的类型 -->
<aggregation_body> <!--聚合体:对哪些字段进行聚合 -->
}
[,"meta" : {[<meta_data_body>] } ]? <!--元 -->
[,"aggregations" : { [<sub_aggregation>]+ } ]? <!--在聚合里面在定义子聚合 -->
}
[,"<aggregation_name_2>" : { ... } ]*<!--聚合的名字 -->
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
说明:aggregations 也可简写为 aggs
# 5.2 指标聚合
# max min sum avg
示例一:查询所有书中最贵的
POST /book/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"max_price": {
"max": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 文档计数count
示例: 统计price大于100的文档数量
POST /book/_count
{
"query": {
"range": {
"price": {
"gt": 100
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# value_count 统计某字段有值的文档数
POST /book/_search?size=0
{
"aggs": {
"price_count": {
"value_count": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# cardinality值去重计数 基数
POST /book/_search?size=0
{
"aggs": {
"_id_count": {
"cardinality": {
"field": "_id"
}
},
"price_count": {
"cardinality": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# stats 统计 count max min avg sum 5个值
POST /book/_search?size=0
{
"aggs": {
"price_stats": {
"stats": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# Extended stats
高级统计,比stats多4个统计结果: 平方和、方差、标准差、平均值加/减两个标准差的区间
POST /book/_search?size=0
{
"aggs": {
"price_stats": {
"extended_stats": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# Percentiles 占比百分位对应的值统计
POST /book/_search?size=0
{
"aggs": {
"price_percents": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
指定分位值
POST /book/_search?size=0
{
"aggs": {
"price_percents": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "price",
"percents": [
75,
99,
99.9
]
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# Percentiles rank 统计值小于等于指定值的文档占比
统计price小于100和200的文档的占比
POST /book/_search?size=0{
"aggs": {
"gge_perc_rank": {
"percentile_ranks": {
"field": "price",
"values": [
100,
200
]
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 5.3 桶聚合
Bucket Aggregations,桶聚合。
它执行的是对文档分组的操作(与sql中的group by类似),把满足相关特性的文档分到一个桶里,即
桶分,输出结果往往是一个个包含多个文档的桶(一个桶就是一个group)
bucket:一个数据分组
metric:对一个数据分组执行的统计
POST /book/_search{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_price": {
"range": {
"field": "price",
"ranges": [
{
"from": 0,
"to": 200
},
{
"from": 200,
"to": 400
},
{
"from": 400,
"to": 1000
}
]
},
"aggs": {
"average_price": {
"avg": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
值的个数统计
"count_price": {
"value_count": {
"field": "price"
}
}
2
3
4
5
实现having 效果
POST /book/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_price": {
"range": {
"field": "price",
"ranges": [
{
"from": 0,
"to": 200
},
{
"from": 200,
"to": 400
},
{
"from": 400,
"to": 1000
}
]
},
"aggs": {
"average_price": {
"avg": {
"field": "price"
}
},
"having": {
"bucket_selector": {
"buckets_path": {
"avg_price": "average_price"
},
"script": {
"source": "params.avg_price >= 200 "
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
# 6 零停机索引重建
# 6.1 说明
Elasticsearch是一个实时的分布式搜索引擎,为用户提供搜索服务,当我们决定存储某种数据时,在创建索引的时候需要数据结构完整确定下来,与此同时索引的设定和很多固定配置将不能改变。当需要改变数据结构时就需要重建索引,为此,Elasticsearch团队提供了辅助工具帮助开发人员进行索引重建。
零停机完成索引重建的三种方案。
# 6.2.方案一:外部数据导入方案
# 1)整体介绍
系统架构设计中,有关系型数据库用来存储数据,Elasticsearch在系统架构里起到查询加速的作用,如果遇到索引重建的操作,待系统模块发布新版本后,可以从数据库将数据查询出来,重新灌到
Elasticsearch即可。
# 2)执行步骤
建议的功能方案:数据库 + MQ + 应用模块 + Elasticsearch,可以在MQ控制台发送MQ消息来触发重导数据,按批次对数据进行导入,整个过程异步化处理,请求操作示意如下所示:
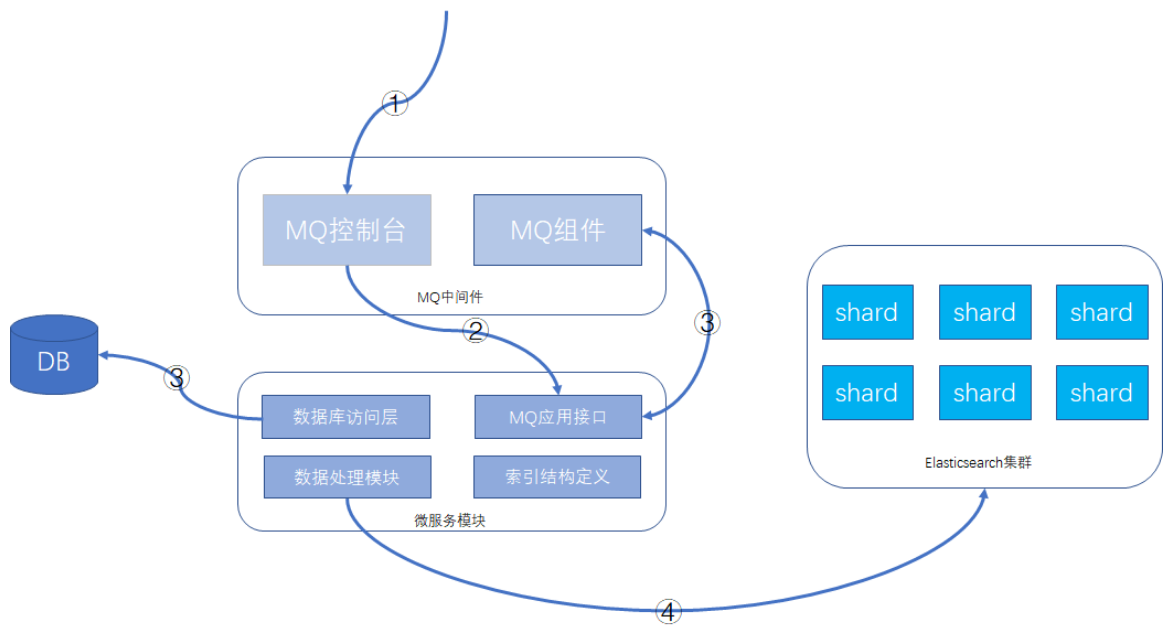
# 3)详细操作步骤:
- 通过MQ的web控制台或cli命令行,发送指定的MQ消息
- MQ消息被微服务模块的消费者消费,触发ES数据重新导入功能
- 微服务模块从数据库里查询数据的总数及批次信息,并将每个数据批次的分页信息重新发送给MQ消息,分页信息包含查询条件和偏移量,此MQ消息还是会被微服务的MQ消息者接收处理。
- 微服务根据接收的查询条件和分页信息,从数据库获取到数据后,根据索引结构的定义,将数据组
装成ES支持的JSON格式,并执行bulk命令,将数据发送给Elasticsearch集群。
这样就可以完成索引的重建工作。
# 4)方案特点
MQ中间件的选型不做具体要求,常见的rabitmq、activemq、rocketmq等均可。
在微服务模块方面,提供MQ消息处理接口、数据处理模块需要事先开发的,一般是创建新的索引时,配套把重建的功能也一起做好。整体功能共用一个topic,针对每个索引,有单独的结构定义和MQ消息处理tag,代码尽可能复用。处理的批次大小需要根据实际的情况设置。
微服务模块实例会部署多个,数据是分批处理的,批次信息会一次性全部先发送给MQ,各个实例处理的数据相互不重叠,利用MQ消息的异步处理机制,可以充分利用并发的优势,加快数据重建的速度。
# 5)方案缺点
- 对数据库造成读取压力,短时间内大量的读操作,会占用数据库的硬件资源,严重时可能引起数据
库性能下降。
- 网络带宽占用多,数据毕竟是从一个库传到另一个库,虽说是内网,但大量的数据传输带宽占用也
需要注意。
- 数据重建时间稍长,跟迁移的数据量大小有关。
# 6.3 方案二:基于scroll+bulk+索引别名方案
# 1)整体介绍
利用Elasticsearch自带的一些工具完成索引的重建工作,当然在方案实际落地时,可能也会依赖客户端的一些功能,比如用Java客户端持续的做scroll查询、bulk命令的封装等。数据完全自给自足,不依赖其他数据源。
# 2)执行步骤
假设原索引名称是book,新的索引名称为book_new,Java客户端使用别名book_alias连接
Elasticsearch,该别名指向原索引book。
- 若Java客户端没有使用别名,需要给客户端分配一个: PUT /book/_alias/book_alias
- 新建索引book_new,将mapping信息,settings信息等按新的要求全部定义好。
- 使用scroll api将数据批量查询出来
为了使用 scroll,初始搜索请求应该在查询中指定 scroll 参数,这可以告诉 Elasticsearch 需要
保持搜索的上下文环境多久,1m 就是一分钟。
GET /book/_search?scroll=1m
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
"_doc"
],
"size": 2
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
- 采用bulk api将scoll查出来的一批数据,批量写入新索引
POST /_bulk
{ "index":
{ "_index": "book_new", "_id": "对应的id值" }}
{ 查询出来的数据值 }
2
3
4
- 反复执行修改后的步骤3和步骤4,查询一批导入一批,以后可以借助Java Client或其他语言的API支持。
注意做3时需要指定上一次查询的 scroll_id
GET /_search/scroll
{
"scroll": "1m",
"scroll_id" : "步骤三中查询出来的值"
}
2
3
4
5
- 切换别名book_alias到新的索引book_new上面,此时Java客户端仍然使用别名访问,也不需要修改任何代码,不需要停机。
POST /_aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"remove": {
"index": "book",
"alias": "book_alias"
}
},
{
"add": {
"index": "book_new",
"alias": "book_alias"
}
}
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
- 验证别名查询的是否为新索引的数据
# 3)方案特点
在数据传输上基本自给自足,不依赖于其他数据源,Java客户端不需要停机等待数据迁移,网络传输占用带宽较小。只是scroll查询和bulk提交这部分,数据量大时需要依赖一些客户端工具。
# 4)补充一点
在Java客户端或其他客户端访问Elasticsearch集群时,使用别名是一个好习惯。
# 6.4 方案三:Reindex API方案
Elasticsearch v6.3.1已经支持Reindex API,它对scroll、bulk做了一层封装,能够 对文档重建索引而不需要任何插件或外部工具。
# 1)最基础的命令:
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "book"
},
"dest": {
"index": "book_new"
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
响应结果:
{
"took": 180,
"timed_out": false,
"total": 4,
"updated": 0,
"created": 4,
"deleted": 0,
"batches": 1,
"version_conflicts": 0,
"noops": 0,
"retries": {
"bulk": 0,
"search": 0
},
"throttled_millis": 0,
"requests_per_second": -1,
"throttled_until_millis": 0,
"failures": []
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
注意: 如果不手动创建新索引book_new的mapping信息,那么Elasticsearch将启动自动映射模板对数据进行类型映射,可能不是期望的类型,这点要注意一下。
# 2)version_type 属性
使用reindex api也是创建快照后再执行迁移的,这样目标索引的数据可能会与原索引有差异,
version_type属性可以决定乐观锁并发处理的规则。
reindex api可以设置version_type属性,如下:
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "book"
},
"dest": {
"index": "book_new",
"version_type": "internal"
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
version_type属性含义如下:
- internal:直接拷贝文档到目标索引,对相同的type、文档ID直接进行覆盖,默认值
- external:迁移文档到目标索引时,保留version信息,对目标索引中不存在的文档进行创建,已存在的文档按version进行更新,遵循乐观锁机制。
# 3)op_type 属性和conflicts 属性
如果op_type设置为create,那么迁移时只在目标索引中创建ID不存在的文档,已存在的文档,会提示错误,如下请求:
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "book"
},
"dest": {
"index": "book_new",
"op_type": "create"
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
有错误提示的响应,节选部分:
{
"took": 11,
"timed_out": false,
"total": 5,
"updated": 0,
"created": 1,
"deleted": 0,
"batches": 1,
"version_conflicts": 4,
"noops": 0,
"retries": {
"bulk": 0,
"search": 0
},
"throttled_millis": 0,
"requests_per_second": -1,
"throttled_until_millis": 0,
"failures": [
{
"index": "book_new",
"type": "children",
"id": "2",
"cause": {
"type": "version_conflict_engine_exception",
"reason": "[children][2]: version conflict, document already exists(current version [17])",
"index_uuid": "dODetUbATTaRL-p8DAEzdA",
"shard": "2",
"index": "book_new"
},
"status": 409
}
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
如果加上"conflicts": "proceed"配置项,那么冲突信息将不展示,只展示冲突的文档数量,请求和响应结果将变成这样:
请求:
POST _reindex
{
"conflicts": "proceed",
"source": {
"index": "book"
},
"dest": {
"index": "book_new",
"op_type": "create"
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
响应:
{
"took": 12,
"timed_out": false,
"total": 5,
"updated": 0,
"created": 1,
"deleted": 0,
"batches": 1,
"version_conflicts": 4,
"noops": 0,
"retries": {
"bulk": 0,
"search": 0
},
"throttled_millis": 0,
"requests_per_second": -1,
"throttled_until_millis": 0,
"failures": []
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# 4)query支持
reindex api支持数据过滤、数据排序、size设置、_source选择等,也支持脚本执行,这里提供一个简单示例:
POST _reindex
{
"size": 100,
"source": {
"index": "book",
"query": {
"term": {
"language": "english"
}
},
"sort": {
"likes": "desc"
}
},
"dest": {
"index": "book_new"
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 6.5 小结
零停机索引重建操作的三个方案,从自研功能、scroll+bulk到reindex,我们作为Elasticsearch的使用者,三个方案的参与度是逐渐弱化的,但稳定性却是逐渐上升的,我们需要清楚地去了解各个方案的优劣,适宜的场景,然后根据实际的情况去权衡,哪个方案更适合我们的业务模型.
# 7 智能搜索建议
现代的搜索引擎,一般会具备"Suggest As You Type"功能,即在用户输入搜索的过程中,进行自动补全或者纠错。 通过协助用户输入更精准的关键词,提高后续全文搜索阶段文档匹配的程度。例如在京东上输入部分关键词,甚至输入拼写错误的关键词时,它依然能够提示出用户想要输入的内容:
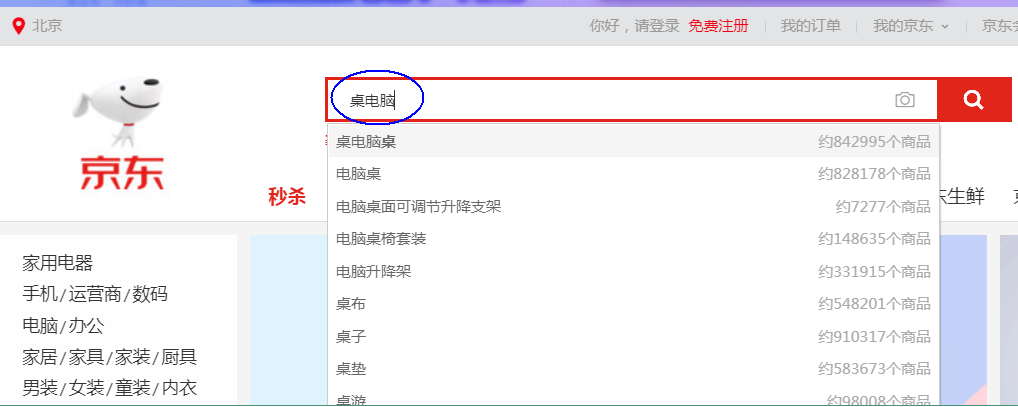
如果自己亲手去试一下,可以看到京东在用户刚开始输入的时候是自动补全的,而当输入到一定长度,如果因为单词拼写错误无法补全,就开始尝试提示相似的词。
那么类似的功能在Elasticsearch里如何实现呢? 答案就在Suggesters API。 Suggesters基本的运作原理是将输入的文本分解为token,然后在索引的字典里查找相似的term并返回。 根据使用场景的不同,Elasticsearch里设计了4种类别的Suggester,分别是:
- Term Suggester
- Phrase Suggester
- Completion Suggester
- Context Suggester
在官方的参考文档里,对这4种Suggester API都有比较详细的介绍,下面的案例将在Elasticsearch 7.x上通过示例讲解Suggester的基础用法,希望能帮助部分国内开发者快速用于实际项目开发。
首先来看一个Term Suggester的示例:
准备一个叫做blogs的索引,配置一个text字段
PUT /blogs/
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"body": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
通过bulk api写入几条文档
POST _bulk/?refresh=true
{ "index" : { "_index" : "blogs" } }
{ "body": "Lucene is cool"}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "blogs" } }
{ "body": "Elasticsearch builds on top of lucene"}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "blogs" } }
{ "body": "Elasticsearch rocks"}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "blogs" } }
{ "body": "Elastic is the company behind ELK stack"}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "blogs" } }
{ "body": "elk rocks"}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "blogs"} }
{ "body": "elasticsearch is rock solid"}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
此时blogs索引里已经有一些文档了,可以进行下一步的探索。为帮助理解,我们先看看哪些term会存在于词典里。
将输入的文本分析一下:
POST _analyze{
"text": [
"Lucene is cool",
"Elasticsearch builds on top of lucene",
"Elasticsearch rocks",
"Elastic is the company behind ELK stack",
"elk rocks",
"elasticsearch is rock solid"
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
这些分出来的token都会成为词典里一个term,注意有些token会出现多次,因此在倒排索引里记录的词频会比较高,同时记录的还有这些token在原文档里的偏移量和相对位置信息。
执行一次suggester搜索看看效果:
POST /blogs/_search
{
"suggest": {
"my-suggestion": {
"text": "lucne rock",
"term": {
"suggest_mode": "missing",
"field": "body"
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
suggest就是一种特殊类型的搜索,DSL内部的"text"指的是api调用方提供的文本,也就是通常用户界面上用户输入的内容。这里的lucne是错误的拼写,模拟用户输入错误。 "term"表示这是一个term suggester。 "field"指定suggester针对的字段,另外有一个可选的"suggest_mode"。 范例里的"missing"实际上就是缺省值,它是什么意思?有点挠头... 还是先看看返回结果吧:
{
"took": 1,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 0,
"max_score": 0,
"hits":
},
"suggest": {
"my-suggestion": [
{
"text": "lucne",
"offset": 0,
"length": 5,
"options": [
{
"text": "lucene",
"score": 0.8,
"freq": 2
}
]
},
{
"text": "rock",
"offset": 6,
"length": 4,
"options":
}
]
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
在返回结果里"suggest" -> "my-suggestion"部分包含了一个数组,每个数组项对应从输入文本分解出来的token(存放在"text"这个key里)以及为该token提供的建议词项(存放在options数组里)。 示例里返回了"lucne","rock"这2个词的建议项(options),其中"rock"的options是空的,表示没有可以建议的选项,为什么? 上面提到了,我们为查询提供的suggest mode是"missing",由于"rock"在索引的词典里已经存在了,够精准,就不建议啦。 只有词典里找不到词,才会为其提供相似的选项。
如果将"suggest_mode"换成"popular"会是什么效果?
尝试一下,重新执行查询,返回结果里"rock"这个词的option不再是空的,而是建议为rocks。
"suggest": {
"my-suggestion": [
{
"text": "lucne",
"offset": 0,
"length": 5,
"options": [
{
"text": "lucene",
"score": 0.8,
"freq": 2
}
]
},
{
"text": "rock",
"offset": 6,
"length": 4,
"options": [
{
"text": "rocks",
"score": 0.75,
"freq": 2
}
]
}
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
回想一下,rock和rocks在索引词典里都是有的。 不难看出即使用户输入的token在索引的词典里已经有了,但是因为存在一个词频更高的相似项,这个相似项可能是更合适的,就被挑选到options里了。
最后还有一个"always" mode,其含义是不管token是否存在于索引词典里都要给出相似项。
有人可能会问,两个term的相似性是如何判断的? ES使用了一种叫做Levenstein edit distance的算法,其核心思想就是一个词改动多少个字符就可以和另外一个词一致。 Term suggester还有其他很多可选参数来控制这个相似性的模糊程度,这里就不一一赘述了。
Phrase suggester在Term suggester的基础上,会考量多个term之间的关系,比如是否同时出现在索引的原文里,相邻程度,以及词频等等。看个范例就比较容易明白了:
POST /blogs/_search
{
"suggest": {
"my-suggestion": {
"text": "lucne and elasticsear rock",
"phrase": {
"field": "body",
"highlight": {
"pre_tag": "<em>",
"post_tag": "</em>"
}
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
返回结果:
"suggest": {
"my-suggestion": [
{
"text": "lucne and elasticsear rock",
"offset": 0,
"length": 26,
"options": [
{
"text": "lucene and elasticsearch rock",
"highlighted": "<em>lucene</em> and <em>elasticsearch</em> rock",
"score": 0.004993905
},
{
"text": "lucne and elasticsearch rock",
"highlighted": "lucne and <em>elasticsearch</em> rock",
"score": 0.0033391973
},
{
"text": "lucene and elasticsear rock",
"highlighted": "<em>lucene</em> and elasticsear rock",
"score": 0.0029183894
}
]
}
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
options直接返回一个phrase列表,由于加了highlight选项,被替换的term会被高亮。因为lucene和elasticsearch曾经在同一条原文里出现过,同时替换2个term的可信度更高,所以打分较高,排在第一位返回。Phrase suggester有相当多的参数用于控制匹配的模糊程度,需要根据实际应用情况去挑选和调试。
下面来谈一下Completion Suggester,它主要针对的应用场景就是"Auto Completion"。 此场景下用户每输入一个字符的时候,就需要即时发送一次查询请求到后端查找匹配项,在用户输入速度较高的情况下对后端响应速度要求比较苛刻。因此实现上它和前面两个Suggester采用了不同的数据结构,索引并非通过倒排来完成,而是将analyze过的数据编码成FST和索引一起存放。对于一个open状态的索引,FST会被ES整个装载到内存里的,进行前缀查找速度极快。但是FST只能用于前缀查找,这也是Completion Suggester的局限所在。
为了使用Completion Suggester,字段的类型需要专门定义如下:
PUT /blogs_completion/
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"body": {
"type": "completion"
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
用bulk API索引点数据:
POST _bulk/?refresh=true
{ "index" : { "_index" : "blogs_completion" } }
{ "body": "Lucene is cool"}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "blogs_completion" } }
{ "body": "Elasticsearch builds on top of lucene"}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "blogs_completion"} }
{ "body": "Elasticsearch rocks"}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "blogs_completion" } }
{ "body": "Elastic is the company behind ELK stack"}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "blogs_completion" } }
{ "body": "the elk stack rocks"}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "blogs_completion"} }
{ "body": "elasticsearch is rock solid"}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
查找:
POST /blogs_completion/_search?pretty
{
"size": 0,
"suggest": {
"blog-suggest": {
"prefix": "elastic i",
"completion": {
"field": "body"
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
结果:
"suggest" : {
"blog-suggest": [
{
"text": "elastic i",
"offset": 0,
"length": 9,
"options": [
{
"text": "Elastic is the company behind ELK stack",
"_index": "blogs_completion",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "7WIhOnQB-DBpPI60CSK-",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"body": "Elastic is the company behind ELK stack"
}
}
]
}
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
值得注意的一点是Completion Suggester在索引原始数据的时候也要经过analyze阶段,取决于选用的analyzer不同,某些词可能会被转换,某些词可能被去除,这些会影响FST编码结果,也会影响查找匹配的效果。
比如我们删除上面的索引,重新设置索引的mapping,将analyzer更改为"english":
PUT /blogs_completion/
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"body": {
"type": "completion",
"analyzer": "english"
}
}
}
}
POST _bulk/?refresh=true
{ "index" : { "_index" : "blogs_completion" } }
{ "body": "Lucene is cool"}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "blogs_completion" } }
{ "body": "Elasticsearch builds on top of lucene"}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "blogs_completion"} }
{ "body": "Elasticsearch rocks"}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "blogs_completion" } }
{ "body": "Elastic is the company behind ELK stack"}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "blogs_completion" } }
{ "body": "the elk stack rocks"}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "blogs_completion"} }
{ "body": "elasticsearch is rock solid"}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
bulk api索引同样的数据后,执行下面的查询:
POST /blogs_completion/_search?pretty
{
"size": 0,
"suggest": {
"blog-suggest": {
"prefix": "elastic i",
"completion": {
"field": "body"
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
居然没有匹配结果了,多么费解! 原来我们用的english analyzer会剥离掉stop word,而is就是其中
一个,被剥离掉了!
用analyze api测试一下:
POST _analyze
{
"text": "elasticsearch is rock solid",
"analyzer":"english"
}
会发现只有3个token:
{
"tokens": [
{
"token": "elasticsearch",
"start_offset": 0,
"end_offset": 13,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 0
},
{
"token": "rock",
"start_offset": 17,
"end_offset": 21,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 2
},
{
"token": "solid",
"start_offset": 22,
"end_offset": 27,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 3
}
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
FST(Finite StateTransducers)只编码了这3个token,并且默认的还会记录他们在文档中的位置和分隔符。 用户输入"elastic i"进行查找的时候,输入被分解成"elastic"和"i",FST没有编码这个“i” , 匹配失败。
好吧,如果你现在还足够清醒的话,试一下搜索"elastic is",会发现又有结果,why? 因为这次输入的
text经过english analyzer的时候is也被剥离了,只需在FST里查询"elastic"这个前缀,自然就可以匹配到了。
其他能影响completion suggester结果的,还有
如"preserve_separators","preserve_position_increments"等等mapping参数来控制匹配的模糊程度。以及搜索时可以选用Fuzzy Queries,使得上面例子里的"elastic i"在使用english analyzer的情况下依然可以匹配到结果。
"preserve_separators": false, 这个设置为false,将忽略空格之类的分隔符
"preserve_position_increments": true,如果建议词第一个词是停用词,并且我们使用了过滤停用词的分析器,需要将此设置为false。
2
3
4
因此用好Completion Sugester并不是一件容易的事,实际应用开发过程中,需要根据数据特性和业务需要,灵活搭配analyzer和mapping参数,反复调试才可能获得理想的补全效果。
回到篇首京东或者百度搜索框的补全/纠错功能,如果用ES怎么实现呢?我能想到的一个的实现方式:
在用户刚开始输入的过程中,使用Completion Suggester进行关键词前缀匹配,刚开始匹配项会比较多,随着用户输入字符增多,匹配项越来越少。如果用户输入比较精准,可能Completion Suggester的结果已经够好,用户已经可以看到理想的备选项了。
如果Completion Suggester已经到了零匹配,那么可以猜测是否用户有输入错误,这时候可以尝试一下Phrase Suggester。如果Phrase Suggester没有找到任何option,开始尝试term Suggester。
精准程度上(Precision)看: Completion > Phrase > term, 而召回率上(Recall)则反之。从性能上看,Completion Suggester是最快的,如果能满足业务需求,只用Completion Suggester做前缀匹配是最理想的。 Phrase和Term由于是做倒排索引的搜索,相比较而言性能应该要低不少,应尽量控制suggester用到的索引的数据量,最理想的状况是经过一定时间预热后,索引可以全量map到内存。
召回率(Recall) = 系统检索到的相关文件 / 系统所有相关的文件总数
准确率(Precision) = 系统检索到的相关文件 / 系统所有检索到的文件总数
从一个大规模数据集合中检索文档时,可把文档分成四组:
- 系统检索到的相关文档(A)
- 系统检索到的不相关文档(B)
- 相关但是系统没有检索到的文档(C)
- 不相关且没有被系统检索到的文档(D)
则:
- 召回率R:用实际检索到相关文档数作为分子,所有相关文档总数作为分母,即R = A / ( A + C )
- 精度P:用实际检索到相关文档数作为分子,所有检索到的文档总数作为分母,即P = A / ( A + B )
举例:一个数据库有 1000 个文档,其中有 50 个文档符合相关定义的问题,系统检索到 75 个文档,但其中只有 45 个文档被检索出。
精度:P=45/75=60%。
召回率:R=45/50=90%。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Context Suggester
- Completion Suggester 的扩展
- 可以在搜索中加入更多的上下文信息,然后根据不同的上下文信息,对相同的输入,比如"star",
提供不同的建议值,比如:
- 咖啡相关:starbucks
- 电影相关:star wars
# 8 Java Client
# 8.1 说明
ES提供多种不同的客户端:
1、TransportClient ES提供的传统客户端,官方计划8.0版本删除此客户端。
2、RestClient RestClient是官方推荐使用的,它包括两种:Java Low Level REST Client和 Java High Level REST Client。 ES在6.0之后提供 Java High Level REST Client, 两种客户端官方更推荐使用 Java High Level REST Client, 使用时加入对应版本的依赖即可。
# 8.2. SpringBoot 中使用 RestClient
# 1)配置 pom.xml
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>7.3.0</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>7.3.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# 2) application.yml文件配置
lagouelasticsearch:
elasticsearch:
hostlist: 192.168.211.138:9200 #多个结点中间用逗号分隔
2
3
# 3)配置类
@Configuration
public class ElasticsearchConfig {
@Value("${lagouelasticsearch.elasticsearch.hostlist}")
private String hostlist;
@Bean
public RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient(){
//解析hostlist配置信息
String[] split = hostlist.split(",");
//创建HttpHost数组,其中存放es主机和端口的配置信息
HttpHost[] httpHostArray = new HttpHost[split.length];
for(int i=0;i<split.length;i++){
String item = split[i];
httpHostArray[i] = new HttpHost(item.split(":")[0], Integer.parseInt(item.split(":")[1]), "http");
}
//创建RestHighLevelClient客户端
return new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(httpHostArray));
}
//项目主要使用RestHighLevelClient,对于低级的客户端暂时不用
@Bean
public RestClient restClient(){
//解析hostlist配置信息
String[] split = hostlist.split(",");
//创建HttpHost数组,其中存放es主机和端口的配置信息
HttpHost[] httpHostArray = new HttpHost[split.length];
for(int i=0;i<split.length;i++){
String item = split[i];
httpHostArray[i] = new HttpHost(item.split(":")[0], Integer.parseInt(item.split(":")[1]), "http");
}
return RestClient.builder(httpHostArray).build();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
# 4) 编写启动类
package com.lagou;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ESApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication.run(ESApplication.class, args);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 5)索引操作
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class TestIndex {
@Autowired
RestHighLevelClient client;
@Autowired
RestClient restClient;
//创建索引库
/*
PUT /elasticsearch_test
{
"settings": {},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"description": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"name": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"pic": {
"type": "text",
"index": false
},
"studymodel": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
*/
@Test
public void testCreateIndex() throws IOException {
//创建索引对象
CreateIndexRequest createIndexRequest = new CreateIndexRequest("elasticsearch_test");
//设置参数
createIndexRequest.settings(Settings.builder().put("number_of_shards","1").put("number_of_replicas","0"));
// 指定映射
XContentBuilder builder = XContentFactory.jsonBuilder()
.startObject()
.field("properties")
.startObject()
.field("studymodel").startObject().field("index", "true").field("type", "keyword").endObject()
.field("name").startObject().field("index", "true").field("type", "integer").endObject()
.field("description").startObject().field("index", "true").field("type", "text").field("analyzer", "ik_max_word").endObject()
.field("pic").startObject().field("index",
"false").field("type", "text").endObject()
.endObject()
.endObject();
createIndexRequest.mapping("doc",builder);
/*指定映射
createIndexRequest.mapping("doc"," {\n" +
" \t\"properties\": {\n" +
"
\"studymodel\":{\n" +
" \"type\":\"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
"
\"name\":{\n" +
" \"type\":\"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"description\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\":\"ik_max_word\" \n" +
" },\n" +
" \"pic\":{\n" +
" \"type\":\"text\",\n" +
" \"index\":false\n" +
" }\n" +
" \t}\n" +
"}", XContentType.JSON);
*/
//操作索引的客户端
IndicesClient indices = client.indices();
//执行创建索引库
//CreateIndexResponse createIndexResponse = indices.create(createIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
CreateIndexResponse createIndexResponse =
indices.create(createIndexRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//得到响应
boolean acknowledged = createIndexResponse.isAcknowledged();
System.out.println(acknowledged);
}
//删除索引库
@Test
public void testDeleteIndex() throws IOException {
//删除索引的请求对象
DeleteIndexRequest deleteIndexRequest = new DeleteIndexRequest("elasticsearch_test");
//操作索引的客户端
IndicesClient indices = client.indices();
//执行删除索引
AcknowledgedResponse delete = indices.delete(deleteIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//得到响应
boolean acknowledged = delete.isAcknowledged();
System.out.println(acknowledged);
}
//添加文档
/*
POST /elasticsearch_test/_doc/1
{
"name": "spring cloud实战",
"description": "本课程主要从四个章节进行讲解: 1.微服务架构入门 2.spring cloud 基础入门 3.实战Spring Boot 4.注册中心eureka。",
"studymodel":"201001",
"timestamp": "2020-08-22 20:09:18",
"price": 5.6
}
*/
@Test
public void testAddDoc() throws IOException {
//创建索引请求对象
IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest("elasticsearch_test","doc");
indexRequest.id("1");
//文档内容 准备json数据
Map<String, Object> jsonMap = new HashMap<>();
jsonMap.put("name", "spring cloud实战");
jsonMap.put("description", "本课程主要从四个章节进行讲解: 1.微服务架构入门 2.spring cloud 基础入门 3.实战Spring Boot 4.注册中心eureka。");
jsonMap.put("studymodel", "201001");
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat =new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
jsonMap.put("timestamp", dateFormat.format(new Date()));
jsonMap.put("price", 5.6f);
indexRequest.source(jsonMap);
//通过client进行http的请求
IndexResponse indexResponse = client.index(indexRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
DocWriteResponse.Result result = indexResponse.getResult();
System.out.println(result);
}
}
//查询文档
@Test
public void testGetDoc() throws IOException {
//查询请求对象
GetRequest getRequest = new GetRequest("elasticsearch_test","2");
GetResponse getResponse = client.get(getRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//得到文档的内容
Map<String, Object> sourceAsMap = getResponse.getSourceAsMap();
System.out.println(sourceAsMap);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
# 6) 其它搜索操作
//搜索全部记录
/*
GET /elasticsearch_test/_search
{
"query":{
"match_all":{}
}
}
*/
@Test
public void testSearchAll() throws IOException, ParseException {
//搜索请求对象
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("elasticsearch_test");
//搜索源构建对象
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//搜索方式
//matchAllQuery搜索全部
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
//设置源字段过虑,第一个参数结果集包括哪些字段,第二个参数表示结果集不包括哪些字段
searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{"name","studymodel","price","timestamp"},new String[]{});
//向搜索请求对象中设置搜索源
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
//执行搜索,向ES发起http请求
SearchResponse searchResponse = client.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//搜索结果
SearchHits hits = searchResponse.getHits();
//匹配到的总记录数
TotalHits totalHits = hits.getTotalHits();
//得到匹配度高的文档
SearchHit[] searchHits = hits.getHits();
//日期格式化对象
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
for(SearchHit hit:searchHits){
//文档的主键
String id = hit.getId();
//源文档内容
Map<String, Object> sourceAsMap = hit.getSourceAsMap();
String name = (String) sourceAsMap.get("name");
//由于前边设置了源文档字段过虑,这时description是取不到的
String description = (String) sourceAsMap.get("description");
//学习模式
String studymodel = (String) sourceAsMap.get("studymodel");
//价格
Double price = (Double) sourceAsMap.get("price");
//日期
Date timestamp = dateFormat.parse((String) sourceAsMap.get("timestamp"));
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(studymodel);
System.out.println(description);
}
}
//TermQuery
@Test
public void testTermQuery() throws IOException, ParseException {
//搜索请求对象
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("elasticsearch_test");
//搜索源构建对象
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//搜索方式
//termQuery
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("name","spring"));
//设置源字段过虑,第一个参数结果集包括哪些字段,第二个参数表示结果集不包括哪些字段
searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{"name","studymodel","price","timestamp"},new String[]{});
//向搜索请求对象中设置搜索源
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
//执行搜索,向ES发起http请求
SearchResponse searchResponse = client.search(searchRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//搜索结果
SearchHits hits = searchResponse.getHits();
//匹配到的总记录数
TotalHits totalHits = hits.getTotalHits();
//得到匹配度高的文档
SearchHit[] searchHits = hits.getHits();
//日期格式化对象
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
for(SearchHit hit:searchHits){
//文档的主键
String id = hit.getId();
//源文档内容
Map<String, Object> sourceAsMap = hit.getSourceAsMap();
String name = (String) sourceAsMap.get("name");
//由于前边设置了源文档字段过虑,这时description是取不到的
String description = (String) sourceAsMap.get("description");
//学习模式
String studymodel = (String) sourceAsMap.get("studymodel");
//价格
Double price = (Double) sourceAsMap.get("price");
//日期
Date timestamp = dateFormat.parse((String) sourceAsMap.get("timestamp"));
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(studymodel);
System.out.println(description);
}
}
//分页查询
@Test
public void testSearchPage() throws IOException, ParseException {
//搜索请求对象
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("elasticsearch_test");
//指定类型
searchRequest.types("doc");
//搜索源构建对象
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//设置分页参数
//页码
int page = 1;
//每页记录数
int size = 2;
//计算出记录起始下标
int from = (page-1)*size;
searchSourceBuilder.from(from);//起始记录下标,从0开始
searchSourceBuilder.size(size);//每页显示的记录数
//搜索方式
//matchAllQuery搜索全部
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
//设置源字段过虑,第一个参数结果集包括哪些字段,第二个参数表示结果集不包括哪些字段
searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{"name","studymodel","price","timestamp"},new String[]{});
//向搜索请求对象中设置搜索源
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
//执行搜索,向ES发起http请求
SearchResponse searchResponse = client.search(searchRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//搜索结果
SearchHits hits = searchResponse.getHits();
//匹配到的总记录数
TotalHits totalHits = hits.getTotalHits();
//得到匹配度高的文档
SearchHit[] searchHits = hits.getHits();
//日期格式化对象
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
for(SearchHit hit:searchHits){
//文档的主键
String id = hit.getId();
//源文档内容
Map<String, Object> sourceAsMap = hit.getSourceAsMap();
String name = (String) sourceAsMap.get("name");
//由于前边设置了源文档字段过虑,这时description是取不到的
String description = (String) sourceAsMap.get("description");
//学习模式
String studymodel = (String) sourceAsMap.get("studymodel");
//价格
Double price = (Double) sourceAsMap.get("price");
//日期
Date timestamp = dateFormat.parse((String) sourceAsMap.get("timestamp"));
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(studymodel);
System.out.println(description);
}
}
//TermQuery 分页
@Test
public void testTermQuery() throws IOException, ParseException {
//搜索请求对象
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("elasticsearch_test");
//搜索源构建对象
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//设置分页参数
//页码
int page = 1;
//每页记录数
int size = 2;
//计算出记录起始下标
int from = (page-1)*size;
searchSourceBuilder.from(from);//起始记录下标,从0开始
searchSourceBuilder.size(size);//每页显示的记录数
//搜索方式
//termQuery
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("name","spring"));
//设置源字段过虑,第一个参数结果集包括哪些字段,第二个参数表示结果集不包括哪些字段
searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{"name","studymodel","price","timestamp"},new String[]{});
//向搜索请求对象中设置搜索源
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
//执行搜索,向ES发起http请求
SearchResponse searchResponse = client.search(searchRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//搜索结果
SearchHits hits = searchResponse.getHits();
//匹配到的总记录数
TotalHits totalHits = hits.getTotalHits();
//得到匹配度高的文档
SearchHit[] searchHits = hits.getHits();
//日期格式化对象
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
for(SearchHit hit:searchHits){
//文档的主键
String id = hit.getId();
//源文档内容
Map<String, Object> sourceAsMap = hit.getSourceAsMap();
String name = (String) sourceAsMap.get("name");
//由于前边设置了源文档字段过虑,这时description是取不到的
String description = (String) sourceAsMap.get("description");
//学习模式
String studymodel = (String) sourceAsMap.get("studymodel");
//价格
Double price = (Double) sourceAsMap.get("price");
//日期
Date timestamp = dateFormat.parse((String) sourceAsMap.get("timestamp"));
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(studymodel);
System.out.println(description);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213

