 Dubbo架构与实战
Dubbo架构与实战
# 1、Dubbo架构概述
# 1.1 什么是Dubbo
Apache Dubbo是一款高性能的Java RPC框架。其前身是阿里巴巴公司开源的一个高性能、轻量级的开源Java RPC框架,可以和Spring框架无缝集成。
# 1.2 dubbo 的特性
参考官网首页 特性一览 (opens new window)
# 1.3 Dubbo 的服务治理
服务治理(SOA governance),企业为了确保项目顺利完成而实施的过程,包括最佳实践、架构原则、治理规程、规律以及其他决定性的因素。服务治理指的是用来管理SOA的采用和实现的过程。
# 2.Dubbo处理流程
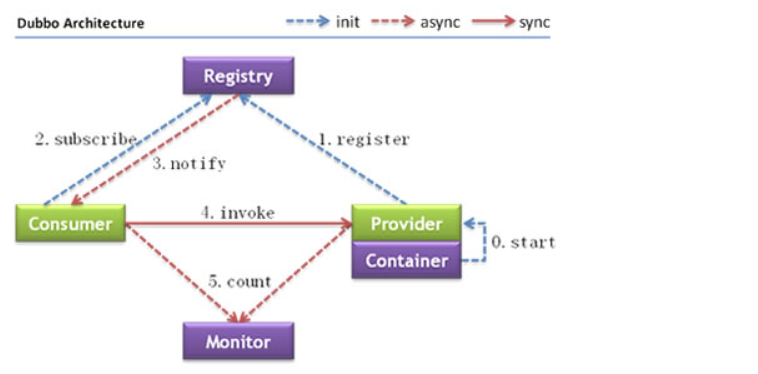
节点说明:
| 节点 | 角色名称 |
|---|---|
| Provider | 暴露服务的服务提供方 |
| Consumer | 调用远程服务的服务消费方 |
| Registry | 服务注册与发现的注册中心 |
| Monitor | 统计服务的调用次数和调用时间的监控中心 |
| Container | 服务运行容器 负责启动 加载 运行服务提供者 |
调用关系说明:
- 虚线 代表异步调用 实线代表同步访问
- 蓝色虚线 是在启动时完成的功能
- 红色虚线 是程序运行中执行的功能
调用流程:
- 服务提供者在服务容器启动时 向注册中心 注册自己提供的服务
- 服务消费者在启动时 向注册中心订阅自己所需的服务
- 注册中心返回服务提供者地址列表给消费者 如果有变更 注册中心会基于长连接推送变更数据给消费者
- 服务消费者 从提供者地址列表中 基于软负载均衡算法 选一台提供者进行调用 如果调用失败 则重新选择一台
- 服务提供者和消费者 在内存中的调用次数 和 调用时间 定时每分钟发送给监控中心
# 3、服务注册中心Zookeeper
通过前面的Dubbo架构图可以看到,Registry(服务注册中心)在其中起着至关重要的作用。Dubbo官方推荐使用Zookeeper作为服务注册中心。Zookeeper 是 Apache Hadoop 的子项目,作为 Dubbo 服务的注册中心,工业强度较高,可用于生产环境,并推荐使用 。
Zookeeper的安装及其使用见上一模块,此处不再赘述。
# 4、Dubbo开发实战
# 4.1 实战案例介绍
在Dubbo中所有的的服务调用都是基于接口去进行双方交互的。双方协定好Dubbo调用中的接口,提供者来提供实现类并且注册到注册中心上。
调用方则只需要引入该接口,并且同样注册到相同的注册中心上(消费者)。即可利用注册中心来实现集群感知功能,之后消费者即可对提供者进行调用。
我们所有的项目都是基于Maven去进行创建,这样相互在引用的时候只需要以依赖的形式进行展现就可以了。
并且这里我们会通过maven的父工程来统一依赖的版本。
程序实现分为以下几步骤:
- 建立maven工程 并且 创建API模块: 用于规范双方接口协定
- 提供provider模块,引入API模块,并且对其中的服务进行实现。将其注册到注册中心上,对外来统一提供服务。
- 提供consumer模块,引入API模块,并且引入与提供者相同的注册中心。再进行服务调用。
# 4.2 开发过程
# 接口协定
- 定义maven。
<groupId>com.lagou</groupId>
<artifactId>service-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
2
3
- 定义接口,这里为了方便,只是写一个基本的方法。
public interface HelloService {
String sayHello(String name);
}
2
3
# 创建接口提供者
- 引入API模块。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.lagou</groupId>
<artifactId>service-api</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
- 引入Dubbo相关依赖,这里为了方便,使用注解方式。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-registry-zookeeper</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-rpc-dubbo</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-remoting-netty4</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-serialization-hessian2</artifactId>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
- 编写实现类。注意这里也使用了Dubbo中的 @Service 注解来声明他是一个服务的提供者。
@Service
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "hello: " + name;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
- 编写配置文件,用于配置dubbo。比如这里我就叫 dubbo-provider.properties ,放入到
resources 目录下。
dubbo.application.name=dubbo-demo-annotation-provider
dubbo.protocol.name=dubbo
dubbo.protocol.port=20880
2
3
- dubbo.application.name: 当前提供者的名称
- dubbo.protocol.name: 对外提供的时候使用的协议
- dubbo.protocol.port: 该服务对外暴露的端口是什么,在消费者使用时,则会使用这个端口并且使用指定的协议与提供者建立连接。
- 编写启动的 main 函数。这里面做的比较简单,主要要注意注解方式中的注册中心这里是使用的本机2181端口来作为注册中心。
public class DubboPureMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ProviderConfiguration.class);
context.start();
System.in.read();
}
@Configuration
@EnableDubbo(scanBasePackages = "com.lagou.service.impl")
@PropertySource("classpath:/dubbo-provider.properties")
static class ProviderConfiguration {
@Bean
public RegistryConfig registryConfig() {
RegistryConfig registryConfig = new RegistryConfig();
registryConfig.setAddress("zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181");
return registryConfig;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# 创建消费者
- 引入API模块。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.lagou</groupId>
<artifactId>service-api</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
- 引入Dubbo依赖 ,同服务提供者。
- 编写服务,用于真实的引用dubbo接口并使用。因为这里是示例,所以比较简单一些。这里面@Reference 中所指向的就是真实的第三方服务接口。
@Component
public class ConsumerComponent {
@Reference
private HelloService helloService;
public String sayHello(String name) {
return helloService.sayHello(name);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
- 编写消费者的配置文件。这里比较简单,主要就是指定了当前消费者的名称和注册中心的位置。通过这个注册中心地址,消费者就会注册到这里并且也可以根据这个注册中心找到真正的提供者列表。
dubbo.application.name=service-consumer
dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
2
- 编写启动类,这其中就会当用户在控制台输入了一次换行后,则会发起一次请求。
public class AnnotationConsumerMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException,
InterruptedException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConsumerConfiguration.class);
context.start();
ConsumerComponent service =
context.getBean(ConsumerComponent.class);
while (true) {
System.in.read();
try {
String hello = service.sayHello("world");
System.out.println("result :" + hello);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Configuration
@EnableDubbo(scanBasePackages = "com.lagou.service")
@PropertySource("classpath:/dubbo-consumer.properties")
@ComponentScan(value = {"com.lagou.bean.consumer"})
static class ConsumerConfiguration {
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# 4.3 配置方式介绍
下面我们来使用不同的方式来对Dubbo进行配置。每种配置方式各有不同,一般可以分为以下几个。
- 注解: 基于注解可以快速的将程序配置,无需多余的配置信息,包含提供者和消费者。但是这种方式有一个弊端,有些时候配置信息并不是特别好找,无法快速定位。
- XML: 一般这种方式我们会和Spring做结合,相关的Service和Reference均使用Spring集成后的。
通过这样的方式可以很方便的通过几个文件进行管理整个集群配置。可以快速定位也可以快速更改。
- 基于代码方式: 基于代码方式的对上述配置进行配置。这个使用的比较少,这种方式更适用于自己公司对其框架与Dubbo做深度集成时才会使用。
# 4.4 XML方式
我们一般XML会结合Spring应用去进行使用,将Service的注册和引用方式都交给Spring去管理。下面我们还是针对于上面的demo进行实现。
这里我们针对于api模块不做处理,还是使用原先的接口。从提供者和消费者做讲解。这了我们直接通过spring的方式去做讲解。
# provider模块
- 引入api依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.lagou</groupId>
<artifactId>service-api</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
- 引入dubbo依赖。与原先的不同点在于,最后多了spring的依赖引入。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-registry-zookeeper</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-registry-nacos</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-rpc-dubbo</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-remoting-netty4</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-serialization-hessian2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-config-spring</artifactId>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
- 编写实现类,不需要引入任何的注解配置。
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "hello: " + name;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
- 编写 dubbo-provider.xml 文件,用于对dubbo进行文件统一配置。并且对刚才的配置进行引入。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo
http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<dubbo:application name="dubbo-demo-annotation-provider"/>
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"/>
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo"/>
<bean id="helloService"
class="com.lagou.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl"/>
<dubbo:service interface="com.lagou.service.HelloService"
ref="helloService"/>
</beans>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
- 编写模块启动类。
public class ProviderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-*.xml");
context.start();
System.in.read();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# consumer模块
- 引入api模块。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.lagou</groupId>
<artifactId>service-api</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
- 引入dubbo相关。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-registry-zookeeper</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-registry-nacos</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-rpc-dubbo</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-remoting-netty4</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-serialization-hessian2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-config-spring</artifactId>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
- 定义spring的配置xml。
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo
http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<dubbo:application name="demo-consumer"/>
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"/>
<dubbo:reference id="helloService"
interface="com.lagou.service.HelloService">
</dubbo:reference>
</beans>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
- 引入启动模块。因为引用了Spring框架,所以再上一步的helloService会被当做一个bean注入到真实的环境中。在我们生产级别使用的时候,我们可以通过Spring中的包扫描机制,通过
@Autowired 这种机制来进行依赖注入。
public class XMLConsumerMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring/dubbo-consumer.xml");
context.start();
HelloService demoService = context.getBean(HelloService.class);
System.out.println(demoService.sayHello("world"));
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 5、Dubbo管理控制台 dubbo-admin
# 5.1 作用
主要包含:服务管理 、 路由规则、动态配置、服务降级、访问控制、权重调整、负载均衡等管理功能
如我们在开发时,需要知道Zookeeper注册中心都注册了哪些服务,有哪些消费者来消费这些服务。我们可以通过部署一个管理中心来实现。其实管理中心就是一个web应用,原来是war(2.6版本以前)包需要部署到tomcat即可。现在是jar包可以直接通过java命令运行。
# 5.2 控制台安装步骤
1.从git 上下载项目 https://github.com/apache/dubbo-admin
2.修改项目下的dubbo.properties文件
注意dubbo.registry.address对应的值需要对应当前使用的Zookeeper的ip地址和端口号
• dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://zk所在机器ip:zk端口
• dubbo.admin.root.password=root
• dubbo.admin.guest.password=guest
3.切换到项目所在的路径 使用mvn 打包
mvn clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true
4.java 命令运行
java -jar 对应的jar包
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
https://hub.docker.com/r/apache/dubbo-admin
docker run -p 8080:8080 apache/dubbo-admin
# 5.3 使用控制台
1.访问http://IP:端口
2.输入用户名root,密码root
3.点击菜单查看服务提供者和服务消费者信息
2
3
# 6.Dubbo配置项说明
# 6.1dubbo:application
对应 org.apache.dubbo.config.ApplicationConfig, 代表当前应用的信息
- name: 当前应用程序的名称,在dubbo-admin中我们也可以看到,这个代表这个应用名称。我们在真正时是时也会根据这个参数来进行聚合应用请求。
- owner: 当前应用程序的负责人,可以通过这个负责人找到其相关的应用列表,用于快速定位到责任人。
- qosEnable : 是否启动QoS 默认true
- qosPort : 启动QoS绑定的端口 默认22222
- qosAcceptForeignIp: 是否允许远程访问 默认是false
# 6.2 dubbo:registry
org.apache.dubbo.config.RegistryConfig, 代表该模块所使用的注册中心。一个模块中的服务可以将其注册到多个注册中心上,也可以注册到一个上。后面再service和reference也会引入这个注册中心。
- id : 当当前服务中provider或者consumer中存在多个注册中心时,则使用需要增加该配置。在一些公司,会通过业务线的不同选择不同的注册中心,所以一般都会配置该值。
- address : 当前注册中心的访问地址。
- protocol : 当前注册中心所使用的协议是什么。也可以直接在 address 中写入,比如使-用zookeeper,就可以写成 zookeeper://xx.xx.xx.xx:2181
- timeout : 当与注册中心不再同一个机房时,大多会把该参数延长。
# 6.3 dubbo:protocol
org.apache.dubbo.config.ProtocolConfig, 指定服务在进行数据传输所使用的协议。
- id : 在大公司,可能因为各个部门技术栈不同,所以可能会选择使用不同的协议进行交互。这里在多个协议使用时,需要指定。
- name : 指定协议名称。默认使用 dubbo 。
# 6.4dubbo:reference
org.apache.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig, 消费者的配置,这里只做简单说明,后面会具体讲解。
- id : 指定该Bean在注册到Spring中的id。
- interface: 服务接口名
- version : 指定当前服务版本,与服务提供者的版本一致。
- registry : 指定所具体使用的注册中心地址。这里面也就是使用上面在 dubbo:registry 中所声明的id。
# 6.5dubbo:service
org.apache.dubbo.config.ServiceConfig, 用于指定当前需要对外暴露的服务信息,后面也会具体讲解。和 dubbo:reference 大致相同。
- interface : 指定当前需要进行对外暴露的接口是什么。
- ref : 具体实现对象的引用,一般我们在生产级别都是使用Spring去进行Bean托管的,所以这里面一般也指的是Spring中的BeanId。
- version : 对外暴露的版本号。不同的版本号,消费者在消费的时候只会根据固定的版本号进行消费。
# 6.6dubbo:method
org.apache.dubbo.config.MethodConfig, 用于在制定的 dubbo:service 或者 dubbo:reference 中的更具体一个层级,指定具体方法级别在进行RPC操作时候的配置,可以理解为对这上面层级中的配置针对于具体方法的特殊处理。
- name : 指定方法名称,用于对这个方法名称的RPC调用进行特殊配置。
- async: 是否异步 默认false
# 6.7 dubbo:service和dubbo:reference详解
这两个在dubbo中是我们最为常用的部分,其中有一些我们必然会接触到的属性。并且这里会讲到一些设置上的使用方案。
- mock: 用于在方法调用出现错误时,当做服务降级来统一对外返回结果,后面我们也会对这个方法做更多的介绍。
- timeout: 用于指定当前方法或者接口中所有方法的超时时间。我们一般都会根据提供者的时长来具体规定。比如我们在进行第三方服务依赖时可能会对接口的时长做放宽,防止第三方服务不稳定导致服务受损。
- check: 用于在启动时,检查生产者是否有该服务。我们一般都会将这个值设置为false,不让其进行检查。因为如果出现模块之间循环引用的话,那么则可能会出现相互依赖,都进行check的话,那么这两个服务永远也启动不起来。
- retries: 用于指定当前服务在执行时出现错误或者超时时的重试机制。
- 注意提供者是否有幂等,否则可能出现数据一致性问题
- 注意提供者是否有类似缓存机制,如出现大面积错误时,可能因为不停重试导致雪崩
- executes: 用于在提供者做配置,来确保最大的并行度。
- 可能导致集群功能无法充分利用或者堵塞
- 但是也可以启动部分对应用的保护功能
- 可以不做配置,结合后面的熔断限流使用

